Hemoglobin binding to A beta and HBG2 SNP association suggest a role in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 17157413
- PMCID: PMC2266611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.10.017
Hemoglobin binding to A beta and HBG2 SNP association suggest a role in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
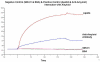
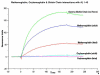
From a normal human brain phage display library screen we identified the gamma (A)-globin chain of fetal hemoglobin (Hb F) as a protein that bound strongly to A beta1-42. We showed the oxidized form of adult Hb (metHb A) binds with greater affinity to A beta1-42 than metHb F. MetHb is more toxic than oxyhemoglobin because it loses its heme group more readily. Free Hb and heme readily damage vascular endothelial cells similar to Alzheimer's disease (AD) vascular pathology. The XmnI polymorphism (C-->T) at -158 of the gamma (G)-globin promoter region can contribute to increased Hb F expression. Using family-based association testing, we found a significant protective association of this polymorphism in the NIMH sibling dataset (n=489) in families, with at least two affected and one unaffected sibling (p=0.006), with an age of onset >50 years (p=0.010) and >65 years (p=0.013), and families not homozygous for the APOE4 allele (p=0.041). We hypothesize that Hb F may be less toxic than adult Hb in its interaction with A beta and may protect against the development of AD.
Figures
References
-
- Adekile AD, Yacoub F, Gupta R, Sinan T, Haider MZ, Habeeb Y, Al-Bloushi M, Moosa A. Silent brain infarcts are rare in Kuwaiti children with sickle cell disease and high Hb F. Am J Hematol. 2002;70(3):228–31. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GJ, Frazer DM. Hepatic iron metabolism. Semin Liver Dis. 2005;25(4):420–32. - PubMed
-
- Azarov I, Huang KT, Basu S, Gladwin MT, Hogg N, Kim-Shapiro DB. Nitric oxide scavenging by red blood cells as a function of hematocrit and oxygenation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(47):39024–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

