HIV inhibits CD4+ T-cell proliferation by inducing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in plasmacytoid dendritic cells
- PMID: 17158233
- PMCID: PMC1852248
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-034785
HIV inhibits CD4+ T-cell proliferation by inducing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in plasmacytoid dendritic cells
Abstract
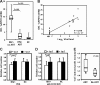
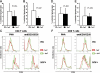
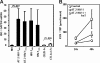
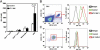
Infection with the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV) results in acute and progressive numeric loss of CD4(+) T-helper cells and functional impairment of T-cell responses. The mechanistic basis of the functional impairment of the surviving cells is not clear. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is an immunosuppressive enzyme that inhibits T-cell proliferation by catabolizing the essential amino acid tryptophan (Trp) into the kynurenine (kyn) pathway. Here, we show that IDO mRNA expression is elevated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from HIV(+) patients compared with uninfected healthy controls (HCs), and that in vitro inhibition of IDO with the competitive blocker 1-methyl tryptophan (1-mT) results in increased CD4(+) T-cell proliferative response in PBMCs from HIV-infected patients. We developed an in vitro model in which exposure of PBMCs from HCs to either infectious or noninfectious, R5- or X4-tropic HIV induced IDO in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). HIV-induced IDO was not inhibited by blocking antibodies against interferon type I or type II, which, however, induced IDO in pDCs when added to PBMC cultures. Blockade of gp120/CD4 interactions with anti-CD4 Ab inhibited HIV-mediated IDO induction. Thus, induction of IDO in pDCs by HIV may contribute to the T-cell functional impairment observed in HIV/AIDS by a non-interferon-dependent mechanism.
Figures

References
-
- Dickmeiss E. Immunology of the human immunodeficiency virus infection. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 1990;15:263–267. - PubMed
-
- Mendila M, Heiken H, Becker S, et al. Immunologic and virologic studies in long-term nonprogressors with HIV-1 infection. Eur J Med Res. 1999;4:417–424. - PubMed
-
- Casseb JS, Benard G, Saito R, et al. The value of the lymphocyte proliferation test with phytohemagglutinin in the immune evaluation of Brazilian HIV-infected patients. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 1995;5:347–349. - PubMed
-
- Janossy G, Borthwick N, Lomnitzer R, et al. Lymphocyte activation in HIV-1 infection, I: predominant proliferative defects among CD45R0+ cells of the CD4 and CD8 lineages. Aids. 1993;7:613–624. - PubMed
-
- Hofmann B, Nishanian P, Baldwin RL, Insixiengmay P, Nel A, Fahey JL. HIV inhibits the early steps of lymphocyte activation, including initiation of inositol phospholipid metabolism. J Immunol. 1990;145:3699–3705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

