A fully integrated microfluidic genetic analysis system with sample-in-answer-out capability
- PMID: 17159153
- PMCID: PMC1748216
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604663103
A fully integrated microfluidic genetic analysis system with sample-in-answer-out capability
Abstract
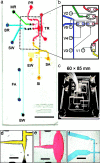
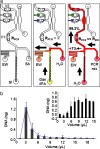
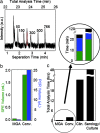
We describe a microfluidic genetic analysis system that represents a previously undescribed integrated microfluidic device capable of accepting whole blood as a crude biological sample with the endpoint generation of a genetic profile. Upon loading the sample, the glass microfluidic genetic analysis system device carries out on-chip DNA purification and PCR-based amplification, followed by separation and detection in a manner that allows for microliter samples to be screened for infectious pathogens with sample-in-answer-out results in < 30 min. A single syringe pump delivers sample/reagents to the chip for nucleic acid purification from a biological sample. Elastomeric membrane valving isolates each distinct functional region of the device and, together with resistive flow, directs purified DNA and PCR reagents from the extraction domain into a 550-nl chamber for rapid target sequence PCR amplification. Repeated pressure-based injections of nanoliter aliquots of amplicon (along with the DNA sizing standard) allow electrophoretic separation and detection to provide DNA fragment size information. The presence of Bacillus anthracis (anthrax) in 750 nl of whole blood from living asymptomatic infected mice and of Bordetella pertussis in 1 microl of nasal aspirate from a patient suspected of having whooping cough are confirmed by the resultant genetic profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Manz A, Graber N, Widmer HM. Sens Act B. 1990;1:244–248.
-
- Lagally ET, Scherer JR, Blazej RG, Toriello NM, Diep BA, Ramchandani M, Sensabaugh GF, Riley LW, Mathies RA. Anal Chem. 2004;76:3162–3170. - PubMed
-
- Pal R, Yang M, Lin R, Johnson BN, Srivastava N, Razzacki SZ, Chomistek KJ, Heldsinger DC, Haque RM, Ugaz VM, et al. Lab Chip. 2005;5:1024–1032. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Enzelberger M, Quake S. Electrophoresis. 2002;23:1531–1536. - PubMed
-
- Auroux PA, Koc Y, deMello A, Manz A, Day PJ. Lab Chip. 2004;4:534–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

