Traditional cardiovascular risk factors in relation to left ventricular mass, volume, and systolic function by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: the Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 17161261
- PMCID: PMC1794681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.072
Traditional cardiovascular risk factors in relation to left ventricular mass, volume, and systolic function by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: the Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Objectives: The goal of this study was to examine the cross-sectional associations of cardiovascular risk factors with left ventricular (LV) geometry and systolic function measured by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA).
Background: Cardiovascular risk factors including hypertension, smoking, and obesity are known to be associated with increased LV mass, but less is known about the association of risk factors with LV systolic function, particularly in populations without clinical cardiovascular disease.
Methods: Participants were from 4 racial/ethnic groups and were free of clinical cardiovascular disease. Blood pressure, health habits, body mass index, lipid levels, and glucose abnormalities were assessed and MRI exams performed at baseline (n = 4,869). Multivariable linear regression was used to model the association of risk factors with LV mass, end-diastolic volume, stroke volume, ejection fraction, and cardiac output.
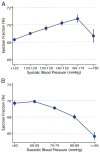
Results: The mean age was 62 years, and 52% of the participants were women. After adjustment for sociodemographic variables and height, higher systolic blood pressure and body mass index were associated with larger LV mass and volumes. Current smoking and diabetes were associated with greater LV mass (+7.7 g, 95% confidence interval [CI] +5.5 to +9.9 and +3.5 g, 95% CI +1.2 to +5.8, respectively), and with lower stroke volume (-1.9 ml, 95% CI -3.3 to -0.5 and -4.5 ml, 95% CI -6.0 to -3.0, respectively) and lower ejection fraction (-1.6%, 95% CI -2.1 to -1.0 and -0.8%, 95% CI -1.5 to -0.2, respectively).
Conclusions: In this cohort free of clinical cardiovascular disease, modifiable risk factors were associated with subclinical alterations in LV size and systolic function as detected by cardiac MRI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gardin JM, Wagenknecht LE, Anton-Culver H, et al. Relationship of cardiovascular risk factors to echocardiographic left ventricular mass in healthy young black and white adult men and women. The CARDIA study. Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults. Circulation. 1995;92:380–7. - PubMed
-
- Gardin JM, Arnold A, Gottdiener JS, et al. Left ventricular mass in the elderly. The Cardiovascular Health Study. Hypertension. 1997;29:1095–103. - PubMed
-
- Savage DD, Levy D, Dannenberg AL, Garrison RJ, Castelli WP. Association of echocardiographic left ventricular mass with body size, blood pressure and physical activity (the Framingham Study) Am J Cardiol. 1990;65:371–6. - PubMed
-
- Pohost GM, Hung L, Doyle M. Clinical use of cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Circulation. 2003;108:647–53. - PubMed
-
- Bild DE, Bluemke DA, Burke GL, et al. Multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis: objectives and design. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;156:871–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases