Developmental and injury-induced expression of alpha1beta1 and alpha6beta1 integrins in the rat spinal cord
- PMID: 17161391
- PMCID: PMC1794000
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.10.072
Developmental and injury-induced expression of alpha1beta1 and alpha6beta1 integrins in the rat spinal cord
Abstract
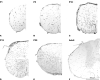
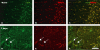
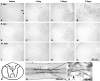
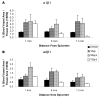
Loss and damage to blood vessels are thought to contribute to secondary tissue loss after spinal cord injury. Integrins might be therapeutic targets to protect the vasculature and/or promote angiogenesis, as their activation can promote tubule formation and survival of endothelial cells in vitro. Here, we show that immunostaining with an antibody against the alpha1beta1 integrin heterodimer is present only in blood vessels from postnatal day 1 (P1) through adulthood in Sprague-Dawley rats. After a spinal cord contusion at T9 in adults, the area of alpha1beta1 integrin positive blood vessels increases within 11 mm from the injury site at 3 days post-injury and remains prominent within the injured core only at 7 days. Staining for the alpha6beta1 integrin heterodimer increases in blood vessels between P10 and adulthood and is present in preganglionic neurons of the intermediolateral cell column (IML) at all ages. The alpha6beta1 integrin is also expressed by motor neurons postnatally, and oligodendrocyte precursors (OPCs), as previously reported. After the contusion, the area of alpha6beta1-stained blood vessels is increased at 3 days and most prominently, 1 mm from the injury site, followed by a significant reduction at 7 days, when alpha6beta1 integrin staining is most prominent around the injured core. Staining is also present in a subset of microglia and/or macrophages. These results raise the possibility that alpha1beta1 and alpha6beta1 integrins in blood vessels might be targeted to reduce blood vessel loss and promote angiogenesis, which may promote tissue sparing after spinal cord injury.
Figures



References
-
- Andreasen SO, Thomsen AR, Koteliansky VE, Novobrantseva TI, Sprague AG, de Fougerolles AR, Christensen JP. Expression and functional importance of collagen-binding integrins, α1β1 and α2β1, on virus-activated T cells. J. Immunol. 2003;171:2804–2811. - PubMed
-
- Baker KA, Hagg T. An adult rat spinal cord contusion model of sensory axon degeneration: a preconditioning lesion or the estrus cycle do not affect outcome. J. Neurotrauma. 2005;22:415–428. - PubMed
-
- Bartholdi D, Rubin BP, Schwab ME. VEGF mRNA induction correlates with changes in the vascular architecture upon spinal cord damage in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997;9:2549–2560. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Horin S, Bank I. The role of very late antigen-1 in immune-mediated inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2004;113:119–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

