Generation and characterization of human monoclonal neutralizing antibodies with distinct binding and sequence features against SARS coronavirus using XenoMouse
- PMID: 17161858
- PMCID: PMC7103293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.09.029
Generation and characterization of human monoclonal neutralizing antibodies with distinct binding and sequence features against SARS coronavirus using XenoMouse
Abstract
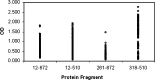
Passive therapy with neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) could be an effective therapy against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV). Utilizing the human immunoglobulin transgenic mouse, XenoMouse, we produced fully human SARS-CoV spike (S) protein specific antibodies. Antibodies were examined for reactivity against a recombinant S1 protein, to which 200 antibodies reacted. Twenty-seven antibodies neutralized 200TCID(50) SARS-CoV (Urbani). Additionally, 57 neutralizing antibodies were found that are likely specific to S2. Mapping of the binding region was achieved with several S1 recombinant proteins. Most S1 reactive neutralizing mAbs bound to the RBD, aa 318-510. However, two S1 specific mAbs reacted with a domain upstream of the RBD between aa 12 and 261. Immunoglobulin gene sequence analyses suggested at least 8 different binding specificities. Unique human mAbs could be used as a cocktail that would simultaneously target several neutralizing epitopes and prevent emergence of escape mutants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular and biological characterization of human monoclonal antibodies binding to the spike and nucleocapsid proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(3):1635-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1635-1644.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15650189 Free PMC article.
-
Antigenic and immunogenic characterization of recombinant baculovirus-expressed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein: implication for vaccine design.J Virol. 2006 Jun;80(12):5757-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00083-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16731915 Free PMC article.
-
Human monoclonal antibody combination against SARS coronavirus: synergy and coverage of escape mutants.PLoS Med. 2006 Jul;3(7):e237. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030237. PLoS Med. 2006. PMID: 16796401 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus: target, mechanism of action, and therapeutic potential.Rev Med Virol. 2012 Jan;22(1):2-17. doi: 10.1002/rmv.706. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Rev Med Virol. 2012. PMID: 21905149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS vaccine development.Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Jul;11(7):1016-20. doi: 10.3201/1107.050219. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16022774 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against highly pathogenic coronaviruses.Curr Opin Virol. 2022 Apr;53:101199. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.12.015. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Curr Opin Virol. 2022. PMID: 35038651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B cell clonal expansion and convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2020 May 6:rs.3.rs-27220. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-27220/v1. Res Sq. 2020. Update in: Cell Host Microbe. 2020 Oct 7;28(4):516-525.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.09.002. PMID: 32702737 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Human B Cell Clonal Expansion and Convergent Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2.Cell Host Microbe. 2020 Oct 7;28(4):516-525.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.09.002. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Cell Host Microbe. 2020. PMID: 32941787 Free PMC article.
-
Human monoclonal antibodies to SARS-coronavirus inhibit infection by different mechanisms.Virology. 2009 Nov 10;394(1):39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.07.028. Epub 2009 Sep 12. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19748648 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 pandemic: lessons learned from more than a century of pandemics and current vaccine development for pandemic control.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Nov;112:300-317. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.09.045. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34563707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baker S.C. Coronaviruses from common colds to severe acute respiratory syndrome. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2004;23:1049–1050. - PubMed
-
- Berry J.D., Jones S., Drebot M.A., Andonov M., Sabara X.Y., Yuan H., Weingartl L., Fernando P., Marszal J., Gren B., Nicolas M., Andonova F., Ranada M.J., Gubbins T.B., Ball P., Kitcdhing Y., Li A., Kabani F., Plummer F. Development and characterization of neutralizing monoclonal antibody to the SARS-coronavirus. J. Virol. Methods. 2004;120:87–96. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan P.K.S., Tang J.W., Hui D.S.C, SARS: clinical presentation, transmission, pathogenesis and treatment options. Clin. Sci. 2006;110:193–204. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

