Characterization of the 12C4 survivin monoclonal antibody and insight into the expression of survivin in human adult tissues
- PMID: 17163847
- PMCID: PMC2826143
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2006.02556.x
Characterization of the 12C4 survivin monoclonal antibody and insight into the expression of survivin in human adult tissues
Abstract
Aims: To elucidate the expression and regulation of survivin in normal tissues.
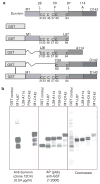
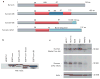
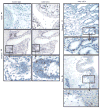
Methods and results: A novel monoclonal antibody (12C4) to survivin was generated. Application of this antibody to determine survivin expression in human normal adult tissues revealed that most adult tissues do not express survivin and, where it is present, survivin is largely restricted to a small subset of epithelial cells and cells with proliferative potential such as thymus. Survivin expression among positive tissues showed individual variations, ranging from zero to < 5% positive cells in epithelial cell populations. Testis is the only human adult tissue highly expressing survivin, with 60-70% positivity in the nuclei of spermatogonia. Consistent with deregulated expression of survivin associated with oncogenesis, we found that certain ligands and transcription factors differentially modulate survivin promoter activity in cancer cells versus normal/untransformed cells.
Conclusion: Deregulation of survivin transcription controls in individual epithelial cells may contribute to oncogenesis in various human adult tissues.
Figures
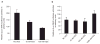
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls of survivin in cancer cells: novel approaches for cancer treatment.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Sep;25(3):391-402. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17167980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new subtype-specific monoclonal antibody for IAP-survivin identifies high-risk patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and improves the prognostic value of bcl-2.Int J Oncol. 2008 Jan;32(1):59-68. Int J Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18097543
-
An HLA-A24-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope of a tumor-associated protein, survivin.Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Jun;8(6):1731-9. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12060610
-
Detection of autoantibodies to livin and survivin in Sera from lung cancer patients.Lung Cancer. 2005 May;48(2):217-21. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.11.002. Epub 2005 Jan 8. Lung Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15829321
-
Survivin and apoptosis control.Adv Cancer Res. 2003;88:31-52. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(03)88303-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12665052 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls of survivin in cancer cells: novel approaches for cancer treatment.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Sep;25(3):391-402. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17167980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DARPP32, STAT5 and STAT3 mRNA expression ratios in glioblastomas are associated with patient outcome.Pathol Oncol Res. 2013 Apr;19(2):329-43. doi: 10.1007/s12253-012-9588-7. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Pathol Oncol Res. 2013. PMID: 23250732 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor gene survivin is highly expressed in adult renal tubular cells: implications for a pathophysiological role in the kidney.Am J Pathol. 2007 Nov;171(5):1483-98. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070132. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17982126 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-oncogene Pokemon promotes breast cancer progression by upregulating survivin expression.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Mar 10;13(2):R26. doi: 10.1186/bcr2843. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21392388 Free PMC article.
-
The apoptosome: emerging insights and new potential targets for drug design.Pharm Res. 2008 Apr;25(4):740-51. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9396-z. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 17674158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, et al. Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 1998;396 (6711):580–584. - PubMed
-
- Li F, Ackermann EJ, Bennett CF, et al. Pleiotropic cell-division defects and apoptosis induced by interference with survivin function. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:461–466. - PubMed
-
- Altieri DC. Survivin, versatile modulation of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene. 2003;22:8581–8589. - PubMed
-
- Altieri DC. Molecular circuits of apoptosis regulation and cell division control: the survivin paradigm. J Cell Biochem. 2004;92:656–663. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med. 1997;3:917–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

