Antigen-specific immunoglobulin E+ B cells are preferentially localized within germinal centres
- PMID: 17163956
- PMCID: PMC2265882
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02509.x
Antigen-specific immunoglobulin E+ B cells are preferentially localized within germinal centres
Abstract
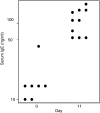
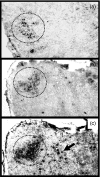
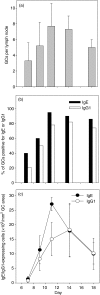
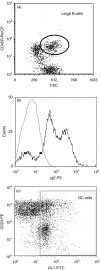
Allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) mediates immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions and plays a central role in allergic diseases. Although antigen-driven B-cell maturation and isotype switching occur within germinal centres (GCs), the role of GCs in IgE production is poorly understood. In view of this, we investigated the development of IgE-expressing cells within GCs in response to an extensively characterized antigen, 2-phenyloxazolone (phOx). The phOx-specific IgE-expressing cells localized within GCs 7 days after immunization, and peaked in number on day 11. Surprisingly, very few IgE-positive cells were found in the T-cell areas of the lymph node. Flow cytometric studies confirmed that IgE was expressed by B cells and was not the result of trapping by follicular dendritic cells. The specificity of the antibody response was confirmed by microdissection and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction using phOx-specific IgE primers. IgE-positive cells were primarily found within GCs while, in contrast, many IgG1-positive cells could also be detected outside GCs in the T-cell areas. Taken together, these data highlight the importance of GCs in the production of antigen-specific IgE antibody.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluorescent in vivo detection reveals that IgE(+) B cells are restrained by an intrinsic cell fate predisposition.Immunity. 2012 May 25;36(5):857-72. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.02.009. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22406270
-
Somatic diversity of the immunoglobulin repertoire is controlled in an isotype-specific manner.Eur J Immunol. 2001 Aug;31(8):2319-30. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200108)31:8<2319::aid-immu2319>3.0.co;2-t. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11477544
-
Is there a typical germinal center? A large-scale immunohistological study on the cellular composition of germinal centers during the hapten-carrier-driven primary immune response in mice.J Immunol. 2011 Dec 15;187(12):6185-96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101440. Epub 2011 Nov 18. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22102720
-
Immunogenetic characteristics of immunoglobulin E in allergic disease.Clin Exp Allergy. 2008 Apr;38(4):566-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.02941.x. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008. PMID: 18261159 Review.
-
Regulation of B lymphocyte differentiation.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000 Apr;84(4):375-85; quiz 385-7. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62267-3. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10795645 Review.
Cited by
-
The production and regulation of IgE by the immune system.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Apr;14(4):247-59. doi: 10.1038/nri3632. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24625841 Review.
-
Crucial role of stimulator of interferon genes-dependent signaling in house dust mite extract-induced IgE production.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 23;11(1):13157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92561-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34162937 Free PMC article.
-
The Developmental History of IgE and IgG4 Antibodies in Relation to Atopy, Eosinophilic Esophagitis, and the Modified TH2 Response.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016 Jun;16(6):45. doi: 10.1007/s11882-016-0621-x. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016. PMID: 27221343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nieuwenhuis P, Opstelten D. Functional anatomy of germinal centers. Am J Anat. 1984;170:421–35. - PubMed
-
- Stedra J, Cerny J. Distinct pathways of B cell differentiation. I. Residual T cells in athymic mice support the development of splenic germinal centers and B cell memory without an induction of antibody. J Immunol. 1994;152:1718–26. - PubMed
-
- Butch AW, Chung GH, Hoffmann JW, Nahm MH. Cytokine expression by germinal center cells. J Immunol. 1993;150:39–47. - PubMed
-
- Decker DJ, Linton PJ, Zaharevitz S, Biery M, Gingeras TR, Klinman NR. Defining subsets of naive and memory B cells based on the ability of their progeny to somatically mutate in vitro. Immunity. 1995;2:195–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

