Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition reveals novel biological functions of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs)
- PMID: 17164131
- PMCID: PMC1904338
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2006.05.004
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition reveals novel biological functions of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs)
Abstract
Early on, intriguing biological activities were found associated with the EETs using in vitro systems. Although the EETs other than the 5,6-isomer, are quite stable chemically, they are quickly degraded enzymatically with the sEH accounting in many cases for much of the metabolism. This rapid degradation often made it difficult to associate biological effects with the administration of EETs and other lipid epoxides particularly in vivo. Thus, it is the power to inhibit the sEH that has facilitated the demonstration of many physiological processes associated with EETs and possibly other epoxy fatty acids. In the last few years it has become clear that major roles of the EETs include modulation of blood pressure and modulation of inflammatory cascades. There are a number of other physiological functions now associated with the EETs including angiogenesis, neurohormone release, cell proliferation, G protein signaling, modulation of ion channel activity, and a variety of effects associated with modulation of NFkappaB. More recently we observed a role of the EETs as modulated by sEHI in reducing non-neuropathic pain. The array of biological effects observed with sEHI illustrates the power of modulating the degradation of chemical mediators in addition to the modulation of their biosynthesis, receptor binding and signal transduction. Many of these biological effects can be modulated by sEHIs but also by the natural eicosanoids and their mimics all of which offer therapeutic potential.
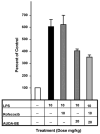
Figures


References
-
- Spector AA, Fang X, Snyder GD, Weintraub NL. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs): metabolism and biochemical function. Progress Lipid Res. 2004;43:55–90. - PubMed
-
- Chacos N, Capdevila J, Falck JR, et al. The reaction of arachidonic acid epoxides (epoxyeicosatrienoic acids) with cytosolic epoxide hydrolase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983;233:639–48. - PubMed
-
- Gill SS, Hammock BD, Casida JE. Mammalian metabolism and environmental degradation of the juvenoid 1-(4′-ethylphenoxy)-3,7-dimethyl-6,7-epoxy-trans-2-octene and related compounds. J Agric Food Chem. 1974;22:386–95. - PubMed
-
- Gill SS, Hammock BD. Distribution and properties of a mammalian soluble epoxide hydrase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980;29:389–95. - PubMed
-
- Arand M, Knehr M, Thomas H, Zeller HD, Oesch F. An impaired peroxisomal targeting sequence leading to an unusual bicompartmental distribution of cytosolic epoxide hydrolase. FEBS Lett. 1991;294:19–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

