Evaluation of fetal arrhythmias from simultaneous pulsed wave Doppler in pulmonary artery and vein
- PMID: 17164485
- PMCID: PMC2016910
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2006.101659
Evaluation of fetal arrhythmias from simultaneous pulsed wave Doppler in pulmonary artery and vein
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the clinical application of simultaneous recordings of pulsed wave Doppler (PWD) signals in pulmonary artery and vein as alternative sampling site for assessment of arrhythmias in the fetus.
Design: Prospective, cross-sectional study.
Setting: Tertiary referral centre for fetal cardiology.
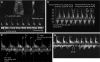
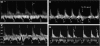
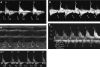
Patients and methods: From July 1999 to July 2005 PWD was used in pulmonary vessels to assess fetal arrhythmias at 15-40 weeks' gestation. Sample volume placement in the peripheral lung vessels was guided by colour flow mapping on a four-chamber section of the fetal heart. Atrial and ventricular systoles were identified from the pulmonary venous and arterial signals respectively. M-mode recordings were used for comparison.
Outcome measures: Diagnosis of fetal arrhythmias.
Results: Of 129 cases, 15 had supraventricular tachycardia, 12 with 1:1 atrioventricular conduction and 3 with atrial flutter and 2:1 block. There were 96 cases of atrial and 7 of ventricular premature beats, 2 of sinus bradycardia, 8 of variable degree heart block and 1 of ventricular tachycardia. PWD was diagnostic in 119 cases. PWD was better than M mode for diagnosis of premature beats and added information about mechanisms of tachycardia. Both methods facilitated interpretation of all arrhythmia patterns, although PWD was of less practical value in cases of complete heart block.
Conclusion: Simultaneous PWD recording of pulmonary vessels in the fetus allows accurate diagnosis of arrhythmias. It is easily obtained with standard ultrasound equipment and adds to the armamentarium of diagnostic techniques for assessment of rhythm abnormalities prenatally.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Comment in
-
Echocardiographic assessment of fetal arrhythmias.Heart. 2007 Nov;93(11):1331-3. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2006.108605. Heart. 2007. PMID: 17933987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeVore G R, Siassi B, Platt L D. Fetal echocardiography. III. The diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmias using real‐time‐directed M‐mode ultrasound. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983146792–799. - PubMed
-
- Kleinman C S, Donnerstein R L, Jaffe C C.et al Fetal echocardiography. A tool for evaluation of in utero cardiac arrhythmias and monitoring of in utero therapy: analysis of 71 patients, Am J Cardiol 198351237–243. - PubMed
-
- Chan F Y, Ghosh A, Tang M.et al Simultaneous pulsed Doppler velocimetry of fetal aorta and inferior vena cava. Diagnosis of fetal congenital heart block; two case reports. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 19903589–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical