A new conceptualization for Mikulicz's disease as an IgG4-related plasmacytic disease
- PMID: 17164992
- PMCID: PMC2785894
- DOI: 10.1007/s10165-006-0518-Y
A new conceptualization for Mikulicz's disease as an IgG4-related plasmacytic disease
Abstract
Mikulicz's disease (MD) has been included within the diagnosis of primary Sjögren's syndrome (SS), but it represents a unique condition involving persistent enlargement of the lacrimal and salivary glands characterized by few autoimmune reactions and good responsiveness to glucocorticoids, leading to the recovery of gland function. Mikulicz's disease was recently reported to be associated with elevated immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) concentrations in the serum and prominent infiltration of plasmacytes expressing IgG4 into the lacrimal and salivary glands. The following features were used for diagnosis: (1) visual confirmation of symmetrical and persistent swelling in more than two lacrimal and major salivary glands; (2) prominent mononuclear cell infiltration of lacrimal and salivary glands; and (3) exclusion of other diseases that present with glandular swelling, such as sarcoidosis and lymphoproliferative disease. These features are not observed in most SS cases. The complications of MD include autoimmune pancreatitis, retroperitoneal fibrosis, tubulointerstitial nephritis, autoimmune hypophysitis, and Riedel's thyroiditis, all of which show IgG4 involvement in their pathogenesis. Mikulicz's disease thus differs from SS and may be a systemic IgG4-related plasmacytic disease.
Figures
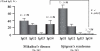

References
-
- Mikulicz J. Über eine eigenartige symmetrishe Erkrankung der Thränen- und Mundspeicheldrüsen. Stuttgart: Beitr. z. Chir. Festschr. f. Theodor Billroth; 1892. pp. 610–30.
-
- Napp O. Über die Beziehungen der Mikuliczschen Erkrankung Tuberkulose. Stschr Augenheilk. 1907;17:513.
-
- Schaffer AJ, Jacobsen AW. Mikulicz's syndrome: a report of ten cases. Am J Dis Child. 1927;34:327–46.
-
- Sjögren H. Zur Kenntnis der Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca (Keratitis filiformis bei Hypofunktion der Tränendrüsen) Acta Ophthalmol. 1933;Suppl II:1–151.

