Quantitative real-time measurements of DNA hybridization with alkylated nonoxidized silicon nanowires in electrolyte solution
- PMID: 17165787
- PMCID: PMC3695614
- DOI: 10.1021/ja065923u
Quantitative real-time measurements of DNA hybridization with alkylated nonoxidized silicon nanowires in electrolyte solution
Abstract
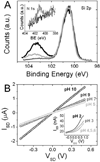
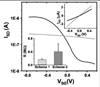
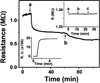
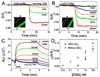
The quantitative, real-time detection of single-stranded oligonucleotides with silicon nanowires (SiNWs) in physiologically relevant electrolyte solution is demonstrated. Debye screening of the hybridization event is circumvented by utilizing electrostatically adsorbed primary DNA on an amine-terminated NW surface. Two surface functionalization chemistries are compared: an amine-terminated siloxane monolayer on the native SiO2 surface of the SiNW, and an amine-terminated alkyl monolayer grown directly on a hydrogen-terminated SiNW surface. The SiNWs without the native oxide exhibit improved solution-gated field-effect transistor characteristics and a significantly enhanced sensitivity to single-stranded DNA detection, with an accompanying 2 orders of magnitude improvement in the dynamic range of sensing. A model for the detection of analyte by SiNW sensors is developed and utilized to extract DNA-binding kinetic parameters. Those values are directly compared with values obtained by the standard method of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and demonstrated to be similar. The nanowires, however, are characterized by higher detection sensitivity. The implication is that SiNWs can be utilized to quantitate the solution-phase concentration of biomolecules at low concentrations. This work also demonstrates the importance of surface chemistry for optimizing biomolecular sensing with silicon nanowires.
Figures



References
-
- Kong J, Franklin NR, Zhou CW, Chapline MG, Peng S, Cho KJ, Dai H. Science. 2000;287:622. - PubMed
-
- Patolsky F, Lieber CM. Mater. Today. 2005;8:20.
-
- Park SJ, Taton TA, Mirkin CA. Science. 2002;295:1503. - PubMed
-
- Ziegler C. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2004;379:946. - PubMed
-
- Lasseter TL, Cai W, Hamers RJ. Analyst. 2004;129:3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

