Deficiency of functional mannose-binding lectin is not associated with infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 17166254
- PMCID: PMC1794530
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2095
Deficiency of functional mannose-binding lectin is not associated with infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
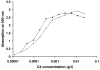
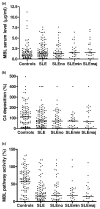
Infection imposes a serious burden on patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The increased infection rate in SLE patients has been attributed in part to defects of immune defence. Recently, the lectin pathway of complement activation has also been suggested to play a role in the occurrence of infections in SLE. In previous studies, SLE patients homozygous for mannose-binding lectin (MBL) variant alleles were at an increased risk of acquiring serious infections in comparison with patients who were heterozygous or homozygous for the normal allele. This association suggests a correlation between functional MBL level and occurrence of infections in SLE patients. We therefore investigated the biological activity of MBL and its relationship with the occurrence of infections in patients with SLE. Demographic and clinical data were collected in 103 patients with SLE. Functional MBL serum levels and MBL-induced C4 deposition were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using mannan as coat and an MBL- or C4b-specific monoclonal antibody. The complete MBL-dependent pathway activity was determined by using an assay that measures the complete MBL pathway activity in serum, starting with binding of MBL to mannan, and was detected with a specific monoclonal antibody against C5b-9. Charts were systematically reviewed to obtain information on documented infections since diagnosis of SLE. Major infections were defined as infections requiring hospital admission and intravenous administration of antibiotics. In total, 115 infections since diagnosis of lupus, including 42 major infections, were documented in the 103 SLE patients (mean age 41 +/- 13 years, mean disease duration 7 +/- 4 years). The percentage of SLE patients with severe MBL deficiency was similar to that in 100 healthy controls: 13% versus 14%, respectively. Although deposition of C4 to mannan and MBL pathway activity were reduced in 21% and 43% of 103 SLE patients, respectively, neither functional MBL serum levels nor MBL pathway activity was associated with infections or major infections in regression analyses. In conclusion, SLE patients frequently suffer from infections, but deficiency of functional MBL does not confer additional risk.
Figures
References
-
- Pryor BD, Bologna SG, Kahl LE. Risk factors for serious infection during treatment with cyclophosphamide and high-dose corticosteroids for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39:1475–1482. - PubMed
-
- Nossent JC. Course and prognostic value of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index in black Caribbean patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1993;23:16–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

