A multicomponent RNA-based control system regulates subgenomic mRNA transcription in a tombusvirus
- PMID: 17166897
- PMCID: PMC1865963
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01969-06
A multicomponent RNA-based control system regulates subgenomic mRNA transcription in a tombusvirus
Abstract
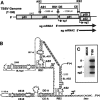
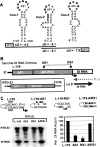
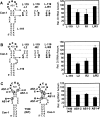
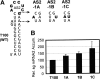
During infections, positive-strand RNA tombusviruses transcribe two subgenomic (sg) mRNAs that allow for the expression of a subset of their genes. This process is thought to involve an unconventional mechanism involving the premature termination of the virally encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase while it is copying the virus genome. The 3' truncated minus strands generated by termination are then used as templates for sg mRNA transcription. In addition to requiring an extensive network of long-distance RNA-RNA interactions (H.-X. Lin and K. A. White, EMBO J. 23:3365-3374, 2004), the transcription of tombusvirus sg mRNAs also involves several additional RNA structures. In vivo analysis of these diverse RNA elements revealed that they function at distinct steps in the process by facilitating the formation or stabilization of the long-distance interactions, modulating minus-strand template production, or promoting the initiation of sg mRNA transcription. All of the RNA elements characterized could be readily incorporated into a premature termination model for sg mRNA transcription. Overall, the analyses revealed a complex system that displays a high level of structural integration and functional coordination. This multicomponent RNA-based control system may serve as a useful paradigm for understanding related transcriptional processes in other positive-sense RNA viruses.
Figures




References
-
- Choi, I. R., M. Ostrovsky, G. Zhang, and K. A. White. 2001. Regulatory activity of distal and core RNA elements in tombusvirus subgenomic mRNA2 transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 276:41761-41768. - PubMed
-
- Choi, I. R., and K. A. White. 2002. An RNA activator of subgenomic mRNA1 transcription in tomato bushy stunt virus. J. Biol. Chem. 277:3760-3766. - PubMed
-
- Fabian, M. R., H. Na, D. Ray, and K. A. White. 2003. 3′-terminal RNA secondary structures are important for accumulation of tomato bushy stunt virus DI RNAs. Virology 313:567-580. - PubMed
-
- Fabian, M. R., and K. A. White. 2004. 5′-3′ RNA-RNA interaction facilitates cap- and poly(A) tail-independent translation of tomato bushy stunt virus mRNA: a potential common mechanism for Tombusviridae. J. Biol. Chem. 279:28862-28872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

