The YLDL sequence within Sendai virus M protein is critical for budding of virus-like particles and interacts with Alix/AIP1 independently of C protein
- PMID: 17166905
- PMCID: PMC1865917
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02218-06
The YLDL sequence within Sendai virus M protein is critical for budding of virus-like particles and interacts with Alix/AIP1 independently of C protein
Abstract
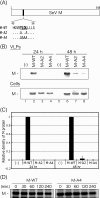
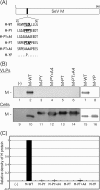
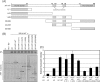
For many enveloped viruses, cellular multivesicular body (MVB) sorting machinery has been reported to be utilized for efficient viral budding. Matrix and Gag proteins have been shown to contain one or two L-domain motifs (PPxY, PT/SAP, YPDL, and FPIV), some of which interact specifically with host cellular proteins involved in MVB sorting, which are recruited to the viral budding site. However, for many enveloped viruses, L-domain motifs have not yet been identified and the involvement of MVB sorting machinery in viral budding is still unknown. Here we show that both Sendai virus (SeV) matrix protein M and accessory protein C contribute to virus budding by physically interacting with Alix/AIP1. A YLDL sequence within the M protein showed L-domain activity, and its specific interaction with the N terminus of Alix/AIP1(1-211) was important for the budding of virus-like particles (VLPs) of M protein. In addition, M-VLP budding was inhibited by the overexpression of some deletion mutant forms of Alix/AIP1 and depletion of endogenous Alix/AIP1 with specific small interfering RNAs. The YLDL sequence was not replaceable by other L-domain motifs, such as PPxY and PT/SAP, and even YPxL. C protein was also able to physically interact with the N terminus of Alix/AIP1(212-357) and enhanced M-VLP budding independently of M-Alix/AIP1 interaction, although it was not released from the transfected cells itself. Our results suggest that the interaction of multiple viral proteins with Alix/AIP1 may enhance the efficiency of the utilization of cellular MVB sorting machinery for efficient SeV budding.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Recruitment of Alix/AIP1 to the plasma membrane by Sendai virus C protein facilitates budding of virus-like particles.Virology. 2008 Feb 5;371(1):108-20. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.09.020. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18028977
-
Significance of the YLDL motif in the M protein and Alix/AIP1 for Sendai virus budding in the context of virus infection.Virology. 2010 Sep 30;405(2):334-41. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.06.031. Virology. 2010. PMID: 20605035
-
AIP1/Alix is a binding partner of Sendai virus C protein and facilitates virus budding.J Virol. 2005 Jul;79(14):8933-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.14.8933-8941.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15994787 Free PMC article.
-
[Envelope virus assembly and budding].Uirusu. 2010 Jun;60(1):105-13. doi: 10.2222/jsv.60.105. Uirusu. 2010. PMID: 20848870 Review. Japanese.
-
Retrovirus budding.Virus Res. 2004 Dec;106(2):87-102. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2004.08.007. Virus Res. 2004. PMID: 15567490 Review.
Cited by
-
Arenavirus budding.Adv Virol. 2011;2011:180326. doi: 10.1155/2011/180326. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Adv Virol. 2011. PMID: 22312335 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for ubiquitin-regulated nuclear and subnuclear trafficking among Paramyxovirinae matrix proteins.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Mar 17;11(3):e1004739. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004739. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25782006 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms for enveloped virus budding: can some viruses do without an ESCRT?Virology. 2008 Mar 15;372(2):221-32. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.11.008. Epub 2007 Dec 11. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18063004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIV5 M protein interaction with host protein angiomotin-like 1.Virology. 2010 Feb 5;397(1):155-66. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.11.002. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Virology. 2010. PMID: 19932912 Free PMC article.
-
Arenavirus budding: a common pathway with mechanistic differences.Viruses. 2013 Jan 31;5(2):528-49. doi: 10.3390/v5020528. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23435234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Babst, M., D. J. Katzmann, E. J. Estepa-Sabal, T. Meerloo, and S. D. Emr. 2002. Escrt-III: an endosome-associated heterooligomeric protein complex required for mvb sorting. Dev. Cell 3:271-282. - PubMed
-
- Babst, M., D. J. Katzmann, W. B. Snyder, B. Wendland, and S. D. Emr. 2002. Endosome-associated complex, ESCRT-II, recruits transport machinery for protein sorting at the multivesicular body. Dev. Cell 3:283-289. - PubMed
-
- Bieniasz, P. D. 2006. Late budding domains and host proteins in enveloped virus release. Virology 344:55-63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

