Degradation of tyrosine phosphatase PTPN3 (PTPH1) by association with oncogenic human papillomavirus E6 proteins
- PMID: 17166906
- PMCID: PMC1865939
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01979-06
Degradation of tyrosine phosphatase PTPN3 (PTPH1) by association with oncogenic human papillomavirus E6 proteins
Abstract
Oncoproteins from DNA tumor viruses associate with critical cellular proteins to regulate cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. Human papillomavirus (HPV) E6 oncoproteins have been previously shown to associate with a cellular HECT domain ubiquitin ligase termed E6AP (UBE3A). Here we show that the E6-E6AP complex associates with and targets the degradation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN3 (PTPH1) in vitro and in living cells. PTPN3 is a membrane-associated tyrosine phosphatase with FERM, PDZ, and PTP domains previously implicated in regulating tyrosine phosphorylation of growth factor receptors and p97 VCP (valosin-containing protein, termed Cdc48 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and is mutated in a subset of colon cancers. Degradation of PTPN3 by E6 requires E6AP, the proteasome, and an interaction between the carboxy terminus of E6 and the PDZ domain of PTPN3. In transduced keratinocytes, E6 confers reduced growth factor requirements, a function that requires the PDZ ligand of E6 and that can in part be replicated by inhibiting the expression of PTPN3. This report demonstrates the potential of E6 to regulate phosphotyrosine metabolism through the targeted degradation of a tyrosine phosphatase.
Figures
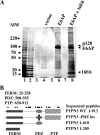

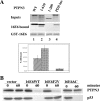

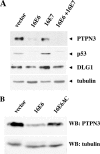

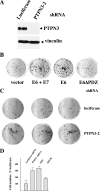
References
-
- Allen-Hoffmann, B. L., S. J. Schlosser, C. A. Ivarie, C. A. Sattler, L. F. Meisner, and S. L. O'Connor. 2000. Normal growth and differentiation in a spontaneously immortalized near-diploid human keratinocyte cell line, NIKS. J. Investig. Dermatol. 114:444-455. - PubMed
-
- Bohl, J., K. Das, B. Dasgupta, and S. B. Vande Pol. 2000. Competitive binding to a charged leucine motif represses transformation by a papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein. Virology 271:163-170. - PubMed
-
- Brooks, L. A., A. Sullivan, J. O'Nions, A. Bell, B. Dunne, J. A. Tidy, D. J. Evans, P. Osin, K. H. Vousden, B. Gusterson, P. J. Farrell, A. Storey, M. Gasco, T. Sakai, and T. Crook. 2002. E7 proteins from oncogenic human papillomavirus types transactivate p73: role in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Br. J. Cancer 86:263-268. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

