The voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.9 is an effector of peripheral inflammatory pain hypersensitivity
- PMID: 17167076
- PMCID: PMC6674969
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4015-06.2006
The voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.9 is an effector of peripheral inflammatory pain hypersensitivity
Abstract
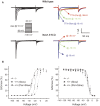
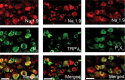
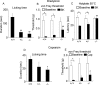
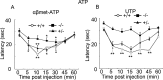
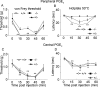
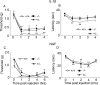
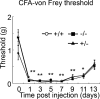
We used a mouse with deletion of exons 4, 5, and 6 of the SCN11A (sodium channel, voltage-gated, type XI, alpha) gene that encodes the voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.9 to assess its contribution to pain. Na(v)1.9 is present in nociceptor sensory neurons that express TRPV1, bradykinin B2, and purinergic P2X3 receptors. In Na(v)1.9-/- mice, the non-inactivating persistent tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium TTXr-Per current is absent, whereas TTXr-Slow is unchanged. TTXs currents are unaffected by the mutation of Na(v)1.9. Pain hypersensitivity elicited by intraplantar administration of prostaglandin E2, bradykinin, interleukin-1beta, capsaicin, and P2X3 and P2Y receptor agonists, but not NGF, is either reduced or absent in Na(v)1.9-/- mice, whereas basal thermal and mechanical pain sensitivity is unchanged. Thermal, but not mechanical, hypersensitivity produced by peripheral inflammation (intraplanatar complete Freund's adjuvant) is substantially diminished in the null allele mutant mice, whereas hypersensitivity in two neuropathic pain models is unchanged in the Na(v)1.9-/- mice. Na(v)1.9 is, we conclude, an effector of the hypersensitivity produced by multiple inflammatory mediators on nociceptor peripheral terminals and therefore plays a key role in mediating peripheral sensitization.
Figures

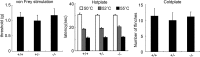
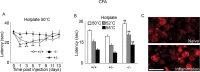
References
-
- Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Wood JN. A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature. 1996;379:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Akopian AN, Souslova V, England S, Okuse K, Ogata N, Ure J, Smith A, Kerr BJ, McMahon SB, Boyce S, Hill R, Stanfa LC, Dickenson AH, Wood JN. The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:541–548. - PubMed
-
- Amaya F, Decosterd I, Samad TA, Plumpton C, Tate S, Mannion RJ, Costigan M, Woolf CJ. Diversity of expression of the sensory neuron-specific TTX-resistant voltage-gated sodium ion channels SNS and SNS2. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000;15:331–342. - PubMed
-
- Amir R, Argoff CE, Bennett GJ, Cummins TR, Durieux ME, Gerner P, Gold MS, Porreca F, Strichartz GR. The role of sodium channels in chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. J Pain. 2006;7:S1–S29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
