E2f1, E2f2, and E2f3 control E2F target expression and cellular proliferation via a p53-dependent negative feedback loop
- PMID: 17167174
- PMCID: PMC1800646
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02147-05
E2f1, E2f2, and E2f3 control E2F target expression and cellular proliferation via a p53-dependent negative feedback loop
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol. 2012 May;32(9):1758
Abstract
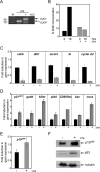
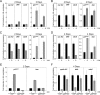
E2F-mediated control of gene expression is believed to have an essential role in the control of cellular proliferation. Using a conditional gene-targeting approach, we show that the targeted disruption of the entire E2F activator subclass composed of E2f1, E2f2, and E2f3 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts leads to the activation of p53 and the induction of p53 target genes, including p21(CIP1). Consequently, cyclin-dependent kinase activity and retinoblastoma (Rb) phosphorylation are dramatically inhibited, leading to Rb/E2F-mediated repression of E2F target gene expression and a severe block in cellular proliferation. Inactivation of p53 in E2f1-, E2f2-, and E2f3-deficient cells, either by spontaneous mutation or by conditional gene ablation, prevented the induction of p21(CIP1) and many other p53 target genes. As a result, cyclin-dependent kinase activity, Rb phosphorylation, and E2F target gene expression were restored to nearly normal levels, rendering cells responsive to normal growth signals. These findings suggest that a critical function of the E2F1, E2F2, and E2F3 activators is in the control of a p53-dependent axis that indirectly regulates E2F-mediated transcriptional repression and cellular proliferation.
Figures





References
-
- Bates, S., A. C. Phillips, P. A. Clark, F. Stott, G. Peters, R. L. Ludwig, and K. H. Vousden.1998. . p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53.Nature 395:124-125. (Letter.) - PubMed
-
- Cam, H., and B. D. Dynlacht. 2003. Emerging roles for E2F: beyond the G1/S transition and DNA replication. Cancer Cell 3:311-316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
