Emerging therapies in gastrointestinal cancers
- PMID: 17167831
- PMCID: PMC4087588
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7440
Emerging therapies in gastrointestinal cancers
Abstract
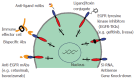
Members of the receptor tyrosine kinase family, that include EGFR, ErbB-2/HER-2, ErbB-3/HER-3 and ErbB-4/HER-4, are frequently implicated in experimental models of epithelial cell neoplasia as well as in human cancers. Therefore, interference with the activation of these growth factor receptors represents a promising strategy for development of novel and selective anticancer therapies. Indeed, a number of inhibitors that target either EGFR or HER-2, with the exception of a few that target both; have been developed for treatment of epithelial cancers. Since most solid tumors express different ErbB receptors and/or their ligands, identification of inhibitor(s), targeting multiple EGFR family members may provide a therapeutic benefit to a broader patient population. Here we describe the significance of an ErbB family of receptors in epithelial cancers, and summarize different available therapeutics targeting these receptors. It also emphasizes the need to develop pan-ErbB inhibitors and discusses EGF-Receptor Related Protein, a recently isolated negative regulator of EGFR as a potential pan-ErbB therapeutic for a wide variety of epithelial cancers.
Figures



References
-
- Schottenfeld D. Gastrointestinal cancer: epidemiology. In: Kelsen DP, Daly JM, Levin B, editors. Gastrointestinal Oncology: Principles and Practice. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2002. pp. 3–24.
-
- Parkin DM, Pisani P, Ferlay J. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 1999;49:33–64, 1. - PubMed
-
- Levin B, Brooks D, Smith RA, Stone A. Emerging technologies in screening for colorectal cancer: CT colonography, immunochemical fecal occult blood tests, and stool screening using molecular markers. CA Cancer J Clin. 2003;53:44–55. - PubMed
-
- Burch PA, Block M, Schroeder G, Kugler JW, Sargent DJ, Braich TA, Mailliard JA, Michalak JC, Hatfield AK, Wright K, et al. Phase III evaluation of octreotide versus chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil or 5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin in advanced exocrine pancreatic cancer: a North Central Cancer Treatment Group study. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:3486–3492. - PubMed
-
- Risch HA. Etiology of pancreatic cancer, with a hypothesis concerning the role of N-nitroso compounds and excess gastric acidity. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:948–960. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

