Alzheimer's presenilin 1 causes chromosome missegregation and aneuploidy
- PMID: 17169464
- PMCID: PMC2692942
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.10.027
Alzheimer's presenilin 1 causes chromosome missegregation and aneuploidy
Abstract
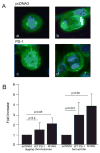
Mutations in the presenilin 1 gene cause most early onset familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD). Here, we report that a defect in the cell cycle - improper chromosome segregation - can be caused by abnormal presenilin function and therefore may contribute to AD pathogenesis. Specifically we find that either over-expression or FAD mutation in presenilin 1 (M146L and M146V) leads to chromosome missegregation and aneuploidy in vivo and in vitro: (1) Up to 20% of lymphocytes and neurons of FAD-PS-1 transgenic and knocking mice are aneuploid by metaphase chromosome analysis and in situ hybridization. (2) Transiently transfected human cells over-expressing normal or mutant PS-1 develop similar aneuploidy within 48 h, including trisomy 21. (3) Mitotic spindles in the PS-1 transfected cells contain abnormal microtubule arrays and lagging chromosomes. Several mechanisms by which chromosome missegregation induced by presenilin may contribute to Alzheimer's disease are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
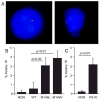
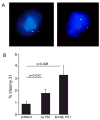
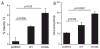
References
-
- Arendt T, Rodel L, Gartner U, Holzer M. Expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 in alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport. 1996;7(18):3047–3049. - PubMed
-
- Chui DH, Tanahashi H, Ozawa K, Ikeda S, Checler F, Ueda O, Suzuki H, Araki W, Inoue H, Shirotani K, Takahashi K, Gallyas F, Tabira T. Transgenic mice with alzheimer presenilin 1 mutations show accelerated neurodegeneration without amyloid plaque formation. Nat Med. 1999;5(5):560–564. - PubMed
-
- Duesberg P. Are centrosomes or aneuploidy the key to cancer? Science. 1999;284(5423):2091–2092. - PubMed
-
- Duff K, Eckman C, Zehr C, Yu X, Prada CM, Perez-tur J, Hutton M, Buee L, Harigaya Y, Yager D, Morgan D, Gordon MN, Holcomb L, Refolo L, Zenk B, Hardy J, Younkin S. Increased amyloid-beta42(43) in brains of mice expressing mutant presenilin 1. Nature. 1996;383(6602):710–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

