Effective regularity in modulation on gastric motility induced by different acupoint stimulation
- PMID: 17171793
- PMCID: PMC4088046
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i47.7642
Effective regularity in modulation on gastric motility induced by different acupoint stimulation
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether manual acupuncture at representative acupoints in different parts of the body can modulate responses of gastric motility in rats and regular effects in different acupoint stimulation.
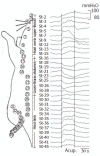
Methods: The gastric motor activity of rats was recorded by the intrapyloric balloon. The changes of gastric motility induced by the stimulation were compared with the background activity in intragastric pressure and/or waves of gastric contraction recorded before any stimulation. Morphological study was also conducted by observing the Evans dye extravasation in the skin after mustard oil injection into the intragastric mucous membrane to certify cutaneous innervations of blue dots related to gastric segmental innervations.
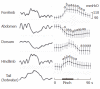
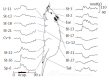
Results: In all six rats that received mustard oil injections into intragastric mucosa, small blue dots appeared in the skin over the whole abdomen, but mainly in peri-midline upper- and middle- abdomen and middle-back, a few in thigh and groin. It may speculate that cutaneous innervations of blue dots have the same distribution as gastric segmental innervations. Acu-stimulation in acupoints of head-neck, four limbs, upper chest-dorsum and lower-dorsum induced markedly augmentation of gastric motility (acupoints on head-neck such as St-2: n = 16, 105.19 +/- 1.36 vs 112.25 +/- 2.02 and St-3: n = 14, 101.5 +/- 1.75 vs 109.36 +/- 1.8; acupoints on limbs such as Sp-6: n = 19, 100.74 +/- 1.54 vs 110.26 +/- 3.88; St-32: n = 17, 103.59 +/- 1.64 vs 108.24 +/- 2.41; St-36: n = 16, 104.81 +/- 1.72 vs 110.81 +/- 2.74 and Li-11: n = 17, 106.47 +/- 2.61 vs 114.77 +/- 3.77, P < 0.05-0.001). Vigorous inhibitory regulations of gastric motility induced by acu-stimulation applied in acupoints on whole abdomen and middle-dorsum were significantly different as compared with the controls before acu-stimulation (abdomen acupoints such as Cv-12: n = 11, 109.36 +/- 2.09 vs 101 +/- 2.21; Cv-6: n = 18, 104.39 +/- 1.42 vs 91.83 +/- 3.22 and St-21: n = 12, 107 +/- 2.97 vs 98.58 +/- 2.81; acupoints on middle-dorsum such as Bl-17: n = 19, 100.63 +/- 1.4 vs 92.21 +/- 2.07 and Bl-21: n = 19, 103.84 +/- 1.48 vs 97.58 +/- 2.16, P < 0.05-0.001).
Conclusion: Regular regulatory effects of facilitation and inhibition on gastric motility appear to be somatotopically organized in the acupoints of whole body, and the effective regularity of site-special acupoints on gastric motility is involved in segmental innervations between stomach and acupoints.
Figures


References
-
- Mayer DJ. Biological mechanisms of acupuncture. Prog Brain Res. 2000;122:457–477. - PubMed
-
- Diehl DL. Acupuncture for gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary disorders. J Altern Complement Med. 1999;5:27–45. - PubMed
-
- Hussain Z, Quigley EM. Systematic review: Complementary and alternative medicine in the irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23:465–471. - PubMed
-
- Gu Y. Treatment of acute abdomen by electro-acupuncture--a report of 245 cases. J Tradit Chin Med. 1992;12:110–113. - PubMed
-
- Jansson G. Extrinsic nervous control of gastric motility. An experimental study in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1969;326:1–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

