Myoelectric activity and motility of the Roux limb after cut or uncut Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy
- PMID: 17171803
- PMCID: PMC4088056
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i47.7699
Myoelectric activity and motility of the Roux limb after cut or uncut Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy
Abstract
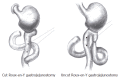
Aim: To explore the mechanisms of uncut Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy, which is used to decrease the occurrence of Roux stasis syndrome.
Methods: The changes of myoelectric activity, mechanic motility and interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) of the Roux limb after cut or uncut Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy were observed.
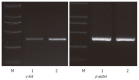
Results: When compared with the cut group, the amplitude (1.15 +/- 0.15 mV vs 0.48 +/- 0.06 mV, P < 0.05) and frequency (14.4 +/- 1.9 cpm vs 9.5 +/- 1.1 cpm, P < 0.01) of slow waves and the incidence (98.2% +/- 10.4% vs 56.6% +/- 6.4%, P < 0.05) and amplitude (0.58 +/- 0.08 mV vs 0.23 +/- 0.06 mV, P < 0.01) of spike potential of the Roux limb in the uncut group were significantly higher. The migrating myoelectric complexes (MMC) phase III duration in the uncut group was significantly prolonged (6.5 +/- 1.1 min vs 4.4 +/- 0.8 min, P < 0.05), while the MMC cycle obviously shortened (42.5 +/- 6.8 vs 55.3 +/- 8.2 min, P < 0.05). Both gastric emptying rate (65.5% +/- 7.9% vs 49.3% +/- 6.8%, P < 0.01) and intestinal impelling ratio (53.4% +/- 7.4% vs 32.2% +/- 5.4%, P < 0.01) in the uncut group were significantly increased. The contractile force index of the isolated jejunal segment in the uncut group was significantly higher (36.8 +/- 5.1 vs 15.3 +/- 2.2, P < 0.01), and the expression of c-kit mRNA was significantly increased in the uncut group (0.82 +/- 0.11 vs 0.35 +/- 0.06, P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Uncut Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy may lessen the effects of operation on myoelectric activity such as slow waves, spike potential, and MMC, decrease the impairment of gastrointestinal motility, and remarkably increase the expression of c-kit mRNA.
Figures



References
-
- Eagon JC, Miedema BW, Kelly KA. Postgastrectomy syndromes. Surg Clin North Am. 1992;72:445–465. - PubMed
-
- Zonca S, Rizzo P. Alteration of the Roux Stasis syndrome by an isolated Roux limb: correlation of slow waves and clinical course. Am Surg. 1999;65:666–672. - PubMed
-
- Kummer EW, Gerritsen JJ, Brummelkamp WH. The cut-closed-reconnected Roux loop. Am J Surg. 2000;179:141–144. - PubMed
-
- Tu BL, Kelly KA. Surgical treatment of Roux stasis syndrome. J Gastrointest Surg. 1999;3:613–617. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

