A suppressor of cell death caused by the loss of sigmaE downregulates extracytoplasmic stress responses and outer membrane vesicle production in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 17172327
- PMCID: PMC1855761
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01534-06
A suppressor of cell death caused by the loss of sigmaE downregulates extracytoplasmic stress responses and outer membrane vesicle production in Escherichia coli
Abstract
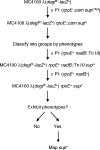
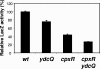
When envelope biogenesis is compromised or damage to envelope components occurs, bacteria trigger signaling cascades, which lead to the production of proteins that combat such extracytoplasmic stresses. In Escherichia coli, there are three pathways known to deal with envelope stresses: the Bae, Cpx, and sigma(E) responses. Although the effectors of the Bae and Cpx responses are not essential in E. coli, the effector of the sigma(E) response, the sigma factor RpoE (sigma(E)), is essential for viability. However, mutations that suppress the lethality of an rpoE-null allele can be easily obtained, and here we describe how we have isolated at least four classes of these suppressors. We present the first description of one such suppressor class, loss-of-function mutations in ydcQ, a gene encoding a putative DNA-binding protein. In wild-type rpoE(+) strains, ydcQ mutants have two distinct phenotypes: extracytoplasmic stress responses are significantly downregulated, and the production of outer membrane vesicles is severely reduced. We present a model in which sigma(E) is not essential per se but, rather, we propose that rpoE mutant cells die, possibly because they overreact to the absence of this sigma factor by triggering a cell death signal.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

