Porin activity of Anaplasma phagocytophilum outer membrane fraction and purified P44
- PMID: 17172334
- PMCID: PMC1855737
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01548-06
Porin activity of Anaplasma phagocytophilum outer membrane fraction and purified P44
Abstract
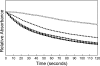
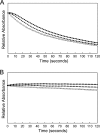
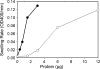
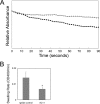
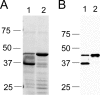
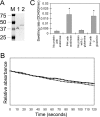
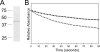
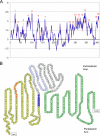
Anaplasma phagocytophilum, an obligatory intracellular bacterium that causes human granulocytic anaplasmosis, has significantly less coding capacity for biosynthesis and central intermediary metabolism than do free-living bacteria. Thus, A. phagocytophilum needs to usurp and acquire various compounds from its host. Here we demonstrate that the isolated outer membrane of A. phagocytophilum has porin activity, as measured by a liposome swelling assay. The activity allows the diffusion of L-glutamine, the monosaccharides arabinose and glucose, the disaccharide sucrose, and even the tetrasaccharide stachyose, and this diffusion could be inhibited with an anti-P44 monoclonal antibody. P44s are the most abundant outer membrane proteins and neutralizing targets of A. phagocytophilum. The P44 protein demonstrates characteristics consistent with porins of gram-negative bacteria, including detergent solubility, heat modifiability, a predicted structure of amphipathic and antiparallel beta-strands, an abundance of polar residues, and a C-terminal phenylalanine. We purified native P44s under two different nondenaturing conditions. When reconstituted into proteoliposomes, both purified P44s exhibited porin activity. P44s are encoded by approximately 100 p44 paralogs and go through extensive antigenic variation. The 16-transmembrane-domain beta-strands consist of conserved P44 N- and C-terminal regions. By looping out the hypervariable region, the porin structure is conserved among diverse P44 proteins yet enables antigenic variation for immunoevasion. The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle of A. phagocytophilum is incomplete and requires the exogenous acquisition of L-glutamine or L-glutamate for function. Efficient diffusion of L-glutamine across the outer membrane suggests that the porin feeds the Anaplasma TCA cycle and that the relatively large pore size provides Anaplasma with the necessary metabolic intermediates from the host cytoplasm.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two monoclonal antibodies with defined epitopes of P44 major surface proteins neutralize Anaplasma phagocytophilum by distinct mechanisms.Infect Immun. 2006 Mar;74(3):1873-82. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1873-1882.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16495562 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplasma phagocytophilum MSP2(P44)-18 predominates and is modified into multiple isoforms in human myeloid cells.Infect Immun. 2008 May;76(5):2090-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01594-07. Epub 2008 Feb 19. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18285495 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and porin activity of P28 and OMP-1F during intracellular Ehrlichia chaffeensis development.J Bacteriol. 2008 May;190(10):3597-605. doi: 10.1128/JB.02017-07. Epub 2008 Mar 21. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18359808 Free PMC article.
-
Type IV secretion in the obligatory intracellular bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilum.Cell Microbiol. 2010 Sep 1;12(9):1213-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01500.x. Epub 2010 Jul 28. Cell Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20670295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solute uptake through general porins.Front Biosci. 2003 May 1;8:d1055-71. doi: 10.2741/1132. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12700124 Review.
Cited by
-
Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia chaffeensis: subversive manipulators of host cells.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 May;8(5):328-39. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2318. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20372158 Review.
-
Anaplasma phagocytophilum Infection Subverts Carbohydrate Metabolic Pathways in the Tick Vector, Ixodes scapularis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Feb 7;7:23. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00023. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28229048 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of complete genome sequence and major surface antigens of Neorickettsia helminthoeca, causative agent of salmon poisoning disease.Microb Biotechnol. 2017 Jul;10(4):933-957. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12731. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Microb Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28585301 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplasma phagocytophilum p44 mRNA expression is differentially regulated in mammalian and tick host cells: involvement of the DNA binding protein ApxR.J Bacteriol. 2007 Dec;189(23):8651-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00881-07. Epub 2007 Sep 28. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17905983 Free PMC article.
-
Possible biased virulence attenuation in the Senegal strain of Ehrlichia ruminantium by ntrX gene conversion from an inverted segmental duplication.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 17;18(2):e0266234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266234. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36800354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbet, A. F., P. F. Meeus, M. Belanger, M. V. Bowie, J. Yi, A. M. Lundgren, A. R. Alleman, S. J. Wong, F. K. Chu, U. G. Munderloh, and S. D. Jauron. 2003. Expression of multiple outer membrane protein sequence variants from a single genomic locus of Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Infect. Immun. 71:1706-1718. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dunning Hotopp, J. C., M. Lin, R. Madupu, J. Crabtree, S. V. Angiuoli, J. Eisen, R. Seshadri, Q. Ren, M. Wu, T. R. Utterback, S. Smith, M. Lewis, H. Khouri, C. Zhang, H. Niu, Q. Lin, N. Ohashi, N. Zhi, W. Nelson, L. M. Brinkac, R. J. Dodson, M. J. Rosovitz, J. Sundaram, S. C. Daugherty, T. Davidsen, A. S. Durkin, M. Gwinn, D. H. Haft, J. D. Selengut, S. A. Sullivan, N. Zafar, L. Zhou, F. Benahmed, H. Forberger, R. Halpin, S. Mulligan, J. Robinson, O. White, Y. Rikihisa, and H. Tettelin. 2006. Comparative genomics of emerging human ehrlichiosis agents. PLoS Genet. 2:e21. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

