IFN-gamma stimulates osteoclast formation and bone loss in vivo via antigen-driven T cell activation
- PMID: 17173138
- PMCID: PMC1697800
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30074
IFN-gamma stimulates osteoclast formation and bone loss in vivo via antigen-driven T cell activation
Abstract
T cell-produced cytokines play a pivotal role in the bone loss caused by inflammation, infection, and estrogen deficiency. IFN-gamma is a major product of activated T helper cells that can function as a pro- or antiresorptive cytokine, but the reason why IFN-gamma has variable effects in bone is unknown. Here we show that IFN-gamma blunts osteoclast formation through direct targeting of osteoclast precursors but indirectly stimulates osteoclast formation and promotes bone resorption by stimulating antigen-dependent T cell activation and T cell secretion of the osteoclastogenic factors RANKL and TNF-alpha. Analysis of the in vivo effects of IFN-gamma in 3 mouse models of bone loss - ovariectomy, LPS injection, and inflammation via silencing of TGF-beta signaling in T cells - reveals that the net effect of IFN-gamma in these conditions is that of stimulating bone resorption and bone loss. In summary, IFN-gamma has both direct anti-osteoclastogenic and indirect pro-osteoclastogenic properties in vivo. Under conditions of estrogen deficiency, infection, and inflammation, the net balance of these 2 opposing forces is biased toward bone resorption. Inhibition of IFN-gamma signaling may thus represent a novel strategy to simultaneously reduce inflammation and bone loss in common forms of osteoporosis.
Figures
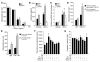
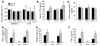
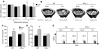
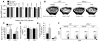

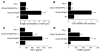
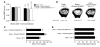
References
-
- Taubman M.A., Kawai T. Involvement of T-lymphocytes in periodontal disease and in direct and indirect induction of bone resorption. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2001;12:125–135. - PubMed
-
- Taubman M.A., Valverde P., Han X., Kawai T. Immune response: the key to bone resorption in periodontal disease. J. Periodontol. 2005;76:2033–2041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

