Effect of various normalization methods on Applied Biosystems expression array system data
- PMID: 17173684
- PMCID: PMC1764432
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-533
Effect of various normalization methods on Applied Biosystems expression array system data
Abstract
Background: DNA microarray technology provides a powerful tool for characterizing gene expression on a genome scale. While the technology has been widely used in discovery-based medical and basic biological research, its direct application in clinical practice and regulatory decision-making has been questioned. A few key issues, including the reproducibility, reliability, compatibility and standardization of microarray analysis and results, must be critically addressed before any routine usage of microarrays in clinical laboratory and regulated areas can occur. In this study we investigate some of these issues for the Applied Biosystems Human Genome Survey Microarrays.
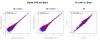
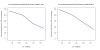
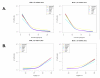
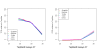
Results: We analyzed the gene expression profiles of two samples: brain and universal human reference (UHR), a mixture of RNAs from 10 cancer cell lines, using the Applied Biosystems Human Genome Survey Microarrays. Five technical replicates in three different sites were performed on the same total RNA samples according to manufacturer's standard protocols. Five different methods, quantile, median, scale, VSN and cyclic loess were used to normalize AB microarray data within each site. 1,000 genes spanning a wide dynamic range in gene expression levels were selected for real-time PCR validation. Using the TaqMan assays data set as the reference set, the performance of the five normalization methods was evaluated focusing on the following criteria: (1) Sensitivity and reproducibility in detection of expression; (2) Fold change correlation with real-time PCR data; (3) Sensitivity and specificity in detection of differential expression; (4) Reproducibility of differentially expressed gene lists.
Conclusion: Our results showed a high level of concordance between these normalization methods. This is true, regardless of whether signal, detection, variation, fold change measurements and reproducibility were interrogated. Furthermore, we used TaqMan assays as a reference, to generate TPR and FDR plots for the various normalization methods across the assay range. Little impact is observed on the TP and FP rates in detection of differentially expressed genes. Additionally, little effect was observed by the various normalization methods on the statistical approaches analyzed which indicates a certain robustness of the analysis methods currently in use in the field, particularly when used in conjunction with the Applied Biosystems Gene Expression System.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Large scale real-time PCR validation on gene expression measurements from two commercial long-oligonucleotide microarrays.BMC Genomics. 2006 Mar 21;7:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-59. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16551369 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-platform comparison of SYBR Green real-time PCR with TaqMan PCR, microarrays and other gene expression measurement technologies evaluated in the MicroArray Quality Control (MAQC) study.BMC Genomics. 2008 Jul 11;9:328. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-328. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18620571 Free PMC article.
-
Cross platform microarray analysis for robust identification of differentially expressed genes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Mar 8;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-S1-S5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17430572 Free PMC article.
-
Normalization and quantification of differential expression in gene expression microarrays.Brief Bioinform. 2006 Jun;7(2):166-77. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbl002. Epub 2006 Mar 7. Brief Bioinform. 2006. PMID: 16772260 Review.
-
Microarray RNA transcriptional profiling: part I. Platforms, experimental design and standardization.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2006 Jul;6(4):535-50. doi: 10.1586/14737159.6.4.535. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2006. PMID: 16824028 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppressive Effect of Quercetin on Nitric Oxide Production from Nasal Epithelial Cells In Vitro.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Jul 5;2018:6097625. doi: 10.1155/2018/6097625. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30069224 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of a molecular classifier obtained by gene expression profiling into a classifier based on real-time PCR: a prognosis predictor for gliomas.BMC Med Genomics. 2010 Nov 10;3:52. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-3-52. BMC Med Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21062501 Free PMC article.
-
Inductive Effect of Palmatine on Apoptosis in RAW 264.7 Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:7262054. doi: 10.1155/2016/7262054. Epub 2016 May 31. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27340419 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a common oligonucleotide reference standard for microarray data normalization and comparison across different microbial communities.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Feb;76(4):1088-94. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02749-09. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20038701 Free PMC article.
-
Large scale immune profiling of infected humans and goats reveals differential recognition of Brucella melitensis antigens.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010 May 4;4(5):e673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000673. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010. PMID: 20454614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang YH, Thorne NP. Normalization for two-color cDNA microarray data. In: Goldstein DR, editor. Science and Statistics: A Festschrift for Terry Speed, IMS Lecture Notes-Monograph Series. Vol. 40. 2003. pp. 403–418.
-
- Hartemink A, Gifford D, Jaakkola T, Young R. Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Optimal Scaling Factors for Expression Array Normalization. In: Bittner M, Chen Y, Dorsel A, Dougherty E, editor. Microarrays: Optical Technologies and Informatics, Proceedings of SPIE. Vol. 4266. 2001. pp. 132–140.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

