Phase II trial of sequential gefitinib after minor response or partial response to chemotherapy in Chinese patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 17173694
- PMCID: PMC1764758
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-288
Phase II trial of sequential gefitinib after minor response or partial response to chemotherapy in Chinese patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Basic research of gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839) has demonstrated the combination effects of gefitinib and chemotherapy were sequence-dependent. To evaluate the efficacy of sequential administration of gefitinib following a minor response or partial response to two to three cycles of chemotherapy, a phase II clinical trial was done in Chinese patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: Thirty-three consecutive patients with advanced NSCLC that had been pretreated with at least one chemotherapeutic regimen and were responding to chemotherapy following 2 to 3 cycles of treatment, entered the trial from May 2004 to February 2006. Patients received gefitinib at an oral dose of 250 mg once daily for 4 weeks.
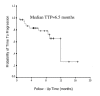
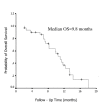
Results: Thirty-three patients were evaluable for response and toxicity. The objective response rate was 24.2% (8 of 33) (95% CI, 11% to 42%). The symptom improvement rate was 54.5% (18 of 33) (95% CI, 41% to 69%). The median duration of response was 7 months (95%CI, 4.0 to 13.2 months). The median time to disease progression (TTP) was 6.5 months (95%CI, 0.7 to 16.6 months). The median overall survival time (OS) was 9.8 months (range, 2.1 to 18.0 months), and the actuarial 1-year survival was 36.4%. Toxicity was relatively mild and included only one patient (3.0%) with grade 4 diarrhea, 1 (3.0%) with grade 3 rash, 1 (3.0%) with grade 3 nausea, and 1 with grade 3 vomiting (3.0%).
Conclusion: Preliminary results suggest that sequential administration of gefitinib following a response to chemotherapy may be beneficial for Chinese patients with advanced NSCLC. Further randomized clinical trials are needed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with gefitinib (ZD1839, "Iressa") on an expanded access study.Lung Cancer. 2004 May;44(2):221-30. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2003.12.014. Lung Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15084387 Clinical Trial.
-
Gefitinib as first-line, compassionate use therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2004 Mar;43(3):317-22. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2003.10.010. Lung Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15165090
-
Evaluation of safety and efficacy of gefitinib ('iressa', zd1839) as monotherapy in a series of Chinese patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: experience from a compassionate-use programme.BMC Cancer. 2004 Aug 19;4:51. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-4-51. BMC Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15318946 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A review of the benefit-risk profile of gefitinib in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Curr Med Res Opin. 2006 Mar;22(3):561-73. doi: 10.1185/030079906X89847. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006. PMID: 16574039 Review.
-
Quality-of-life benefits and evidence of antitumour activity for patients with brain metastases treated with gefitinib.Br J Cancer. 2003 Dec;89 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S15-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601478. Br J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 14661048 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pruritus in patients treated with targeted cancer therapies: systematic review and meta-analysis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Nov;69(5):708-720. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.038. Epub 2013 Aug 24. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23981682 Free PMC article.
-
Gefitinib in non-small-cell lung cancer-an old lesson new re-visited.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2013 Dec;2(6):435-8. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2013.10.01. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 25806264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberola V, Camps C, Provencio M, Isla D, Rosell R, Vadell C, Bover I, Ruiz-Casado A, Azaqra P, Jimenez U, Gonzalez-Larriba JL, Diz P, Cardenal F, Artal A, Carrato A, morales S, Sanchez JJ, de las Penas A, Felip E, lopez-Vivanco G, Spanish Lung Cancer group Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus a cisplatin-based triplet versus nonplatinum sequential doublets in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a Spanish Lung Cancer Group phase III randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3207–3213. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.12.038. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cullen MH, Billingham LJ, Woodroffe CM, Chetiyawardana AD, Gower NH, Joshi R, Ferry DR, Rudd RM, Spiro SG, Cook JE, Trask C, Bessell E, Connolly CK, Tobias J, Souhami RL. Mitomycin, ifosfamide and cisplatin in unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer: Effects on survival and quality of life. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:3188–3194. - PubMed
-
- Georgoulias V, Papadakis E, Alexopoulos A, Tsiafaki X, Rapti A, Veslemes M, Palamidas P, Vlachonikolis I, Greek Oncology Cooperative Group (GOCG) for Lung cancer Platinum-based and non-platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2001;357:1478–1484. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04644-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Georgoulias V, Ardavanis A, Agelidou A, Agelidou M, Chandrinos V, Tsaroucha E, Toumbis M, Kouroussis C, Syrigos K, Polyzos A, Samaras N, Papakotoulas P, Christofilakis C, Ziras N, Alegakis A. Docetaxel versus docetaxel plus cisplatin as front-line treatment of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomized, multicenter phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:2602–2609. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.11.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical