Quantitative continuous assay for hyaluronan synthase
- PMID: 17173853
- PMCID: PMC4114249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2006.11.011
Quantitative continuous assay for hyaluronan synthase
Abstract
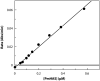
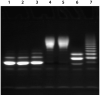
A rapid, continuous, and convenient three-enzyme coupled UV absorption assay was developed to quantitate the glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine transferase activities of hyaluronan synthase from Pasteurella multocida (PmHAS). Activity was measured by coupling the UDP produced from the PmHAS-catalyzed transfer of UDP-GlcNAc and UDP-GlcUA to a hyaluronic acid tetrasaccharide primer with the oxidation of NADH. Using a fluorescently labeled primer, the products were characterized by gel electrophoresis. Our results show that a truncated soluble form of recombinant PmHAS (residues 1-703) can catalyze the glycosyl transfers in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. The assay can be used to determine kinetic parameters, inhibition constants, and mechanistic aspects of this enzyme. In addition, it can be used to quantify PmHAS during purification of the enzyme from culture media.
Figures
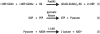




Similar articles
-
Analysis of the two active sites of the hyaluronan synthase and the chondroitin synthase of Pasteurella multocida.Glycobiology. 2003 Oct;13(10):661-71. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwg085. Epub 2003 Jun 10. Glycobiology. 2003. PMID: 12799342
-
Critical elements of oligosaccharide acceptor substrates for the Pasteurella multocida hyaluronan synthase.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 3;281(9):5391-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510439200. Epub 2005 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16361253
-
Dissection of the two transferase activities of the Pasteurella multocida hyaluronan synthase: two active sites exist in one polypeptide.Glycobiology. 2000 Sep;10(9):883-9. doi: 10.1093/glycob/10.9.883. Glycobiology. 2000. PMID: 10988250
-
The dynamic metabolism of hyaluronan regulates the cytosolic concentration of UDP-GlcNAc.Matrix Biol. 2014 Apr;35:14-7. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.01.014. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24486448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic control of hyaluronan synthases.Matrix Biol. 2014 Apr;35:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24134926 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the polymerization initiation and activity of Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase PmHS2, an enzyme with glycosyltransferase and UDP-sugar hydrolase activity.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 21;286(3):1777-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.136754. Epub 2010 Nov 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21084307 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro synthesis of heparosan using recombinant Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase PmHS2.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Feb;85(6):1881-91. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2214-2. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 19756580 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Characterization of the Amount and Length of (1,3)-β-d-glucan for Functional and Mechanistic Analysis of Fungal (1,3)-β-d-glucan Synthase.Bio Protoc. 2021 Apr 20;11(8):e3995. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3995. eCollection 2021 Apr 20. Bio Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34124296 Free PMC article.
-
Elastographic Assessment of Xenograft Pancreatic Tumors.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2017 Dec;43(12):2891-2903. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2017.08.008. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28964615 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of heparosan oligosaccharides by Pasteurella multocida PmHS2 single-action transferases.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Sep;95(5):1199-210. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3813-2. Epub 2011 Dec 24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22198719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toyokawa K, Harayama H, Miyake M. Exogenous hyaluronic acid enhances porcine parthenogenetic embryo development in vitro possibly mediated by CD44. Theriogenology. 2005;64:378–392. - PubMed
-
- Taylor KR, Gallo RL. Glycosaminoglycans and their proteoglycans: host-associated molecular patterns for initiation and modulation of inXammation. FASEB J. 2006;20:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Price RD, Myers S, Leigh IM, Navsaria HA. The role of hyaluronic acid in wound healing: assessment of clinical evidence. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2005;6:393–402. - PubMed
-
- Yabushita H, Kishida T, Fusano K, Kanyama K, Zhuo L, Itano N, Kimata K, Noguchi MY. Role of hyaluronan and hyaluronan synthase in endometrial cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2005;13:1101–1105. - PubMed
-
- Adamia S, Maxwell CA, Pilarski LM. Hyaluronan and hyaluronan synthases: potential therapeutic targets in cancer. Curr. Drug Targets Cardiovasc. Haematol. Disord. 2005;5:3–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

