4-Hydroxynonenal, a product of oxidative stress, leads to an antioxidant response in optic nerve head astrocytes
- PMID: 17173895
- PMCID: PMC1832079
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2006.10.020
4-Hydroxynonenal, a product of oxidative stress, leads to an antioxidant response in optic nerve head astrocytes
Abstract
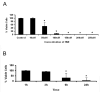
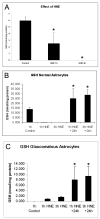
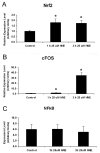
Oxidative stress has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative disorders including primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) an optic neuropathy characterized by loss of retinal ganglion cell (RGC) axons and remodeling of the optic nerve head (ONH). Previous findings in glaucomatous astrocytes suggested increased oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in human optic nerves. We studied the dose and time dependent effects of 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE), a by-product of lipid peroxidation, on the viability of primary cultures of human ONH astrocyte. A significant depletion of glutathione (GSH) level was observed in normal astrocytes after exposure to HNE for 1 h and 3 h. Untreated glaucomatous astrocytes exhibited depleted levels of GSH which increased slightly after exposure to HNE. Both normal and glaucomatous astrocytes recovered GSH levels after 24 h of removal of HNE. HNE caused significant increases in expression of antioxidant enzymes, glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC), aldo-keto reductase 1C family member 1 (AKR1C1) and glutathione S-transferase-alpha4 (GSTA4). HNE induced expression of the transcription factor Nrf2, which coordinates the upregulation of detoxification enzymes. In addition, ONH astrocytes responded to HNE by activation and transcription of cFOS and NFkB, which regulate physiological protective responses against oxidative stress. Our results indicate that ONH astrocytes exhibit a strong antioxidant response to HNE treatment by inducing the transcription factors cFOS, NFkB, and Nrf2, which upregulate the expression of GCLC, to produce more GSH in the cell. AKR1C1 was also upregulated after HNE treatment to inactivate HNE, independent of GSH availability in the cells. Collectively these data indicate that ONH astrocytes can efficiently counteract the neurotoxic effects of HNE offering protection in the optic nerve by releasing GSH and antioxidant enzymes to eliminate the products of chronic oxidative stress.
Figures


References
-
- Agapova OA, Ricard CS, Salvador-Silva M, Hernandez MR. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human optic nerve head astrocytes. Glia. 2001;33:205–216. - PubMed
-
- Agapova OA, Yang P, Wang WH, Lane DA, Clark AF, Weinstein BI, Hernandez MR. Altered expression of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in human glaucomatous optic nerve head astrocytes. Neurobiol Dis. 2003;14:63–73. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed I, John A, Vijayasarathy C, Robin MA, Raza H. Differential modulation of growth and glutathione metabolism in cultured rat astrocytes by 4-hydroxynonenal and green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Neurotoxicology. 2002;23:289–300. - PubMed
-
- Bolanos JP, Heales SJ, Peuchen S, Barker JE, Land JM, Clark JB. Nitric oxide-mediated mitochondrial damage: a potential neuroprotective role for glutathione. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996;21:995–1001. - PubMed
-
- Burczynski ME, Sridhar GR, Palackal NT, Penning TM. The reactive oxygen species--and Michael acceptor-inducible human aldoketo reductase AKR1C1 reduces the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehyde 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal to 1,4-dihydroxy-2-nonene. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:2890–2897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

