Detection of prodromal Alzheimer's disease via pattern classification of magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 17174012
- PMCID: PMC2323584
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.11.010
Detection of prodromal Alzheimer's disease via pattern classification of magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
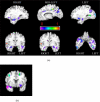
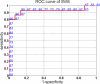
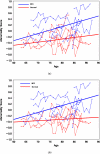
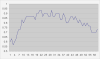
We report evidence that computer-based high-dimensional pattern classification of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) detects patterns of brain structure characterizing mild cognitive impairment (MCI), often a prodromal phase of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Ninety percent diagnostic accuracy was achieved, using cross-validation, for 30 participants in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Retrospective evaluation of serial scans obtained during prior years revealed gradual increases in structural abnormality for the MCI group, often before clinical symptoms, but slower increase for individuals remaining cognitively normal. Detecting complex patterns of brain abnormality in very early stages of cognitive impairment has pivotal importance for the detection and management of AD.
Figures


References
-
- Ashburner J, Csernansky JG, Davatzikos C, Fox NC, Frisoni GB, Thompson PM. Computer-assisted imaging to assess brain structure in healthy and diseased brains. The Lancet (Neurology) 2003;2(2):79–88. - PubMed
-
- Bobinski M, de Leon MJ, Convit A, De Santi S, Wegiel J, Tarshish CY, Saint Louis LA, Wisniewski HM. MRI of entorhinal cortex in mild Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1999;353(9146):38–40. - PubMed
-
- Bookstein FL. ‘Voxel-Based Morphometry’ Should Not Be Used With Imperfectly Registered Images. Neuroimage. 2001;14:1454–62. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E, Bohl J, Bratzke H. Evolution of Alzheimer's disease related cortical lesions. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1998;54:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Chetelat G. Early diagnosis of Alzheiner's Disease: contribution of structural neuroimaging. Neuroimage. 2003;18(2):525–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

