Amino acid contribution to protein solubility: Asp, Glu, and Ser contribute more favorably than the other hydrophilic amino acids in RNase Sa
- PMID: 17174328
- PMCID: PMC2771383
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.10.026
Amino acid contribution to protein solubility: Asp, Glu, and Ser contribute more favorably than the other hydrophilic amino acids in RNase Sa
Abstract
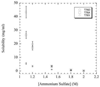
Poor protein solubility is a common problem in high-resolution structural studies, formulation of protein pharmaceuticals, and biochemical characterization of proteins. One popular strategy to improve protein solubility is to use site-directed mutagenesis to make hydrophobic to hydrophilic mutations on the protein surface. However, a systematic investigation of the relative contributions of all 20 amino acids to protein solubility has not been done. Here, 20 variants at the completely solvent-exposed position 76 of ribonuclease (RNase) Sa are made to compare the contributions of each amino acid. Stability measurements were also made for these variants, which occur at the i+1 position of a type II beta-turn. Solubility measurements in ammonium sulfate solutions were made at high positive net charge, low net charge, and high negative net charge. Surprisingly, there was a wide range of contributions to protein solubility even among the hydrophilic amino acids. The results suggest that aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and serine contribute significantly more favorably than the other hydrophilic amino acids especially at high net charge. Therefore, to increase protein solubility, asparagine, glutamine, or threonine should be replaced with aspartic acid, glutamic acid or serine.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The effect of net charge on the solubility, activity, and stability of ribonuclease Sa.Protein Sci. 2001 Jun;10(6):1206-15. doi: 10.1110/ps.440101. Protein Sci. 2001. PMID: 11369859 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring and increasing protein solubility.J Pharm Sci. 2008 Oct;97(10):4155-66. doi: 10.1002/jps.21327. J Pharm Sci. 2008. PMID: 18240286 Review.
-
Charge-charge interactions are key determinants of the pK values of ionizable groups in ribonuclease Sa (pI=3.5) and a basic variant (pI=10.2).J Mol Biol. 2003 Jan 31;325(5):1077-92. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01273-1. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12527309
-
Conservation of amino acids in multiple alignments: aspartic acid has unexpected conservation.FEBS Lett. 1996 Nov 18;397(2-3):225-9. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(96)01181-7. FEBS Lett. 1996. PMID: 8955352
-
Effect of the replacement of aspartic acid/glutamic acid residues with asparagine/glutamine residues in RNase He1 from Hericium erinaceus on inhibition of human leukemia cell line proliferation.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015;79(2):211-7. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2014.972327. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25338779
Cited by
-
Engineered Autonomous Human Variable Domains.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(43):6527-6537. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160921143011. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 27655414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PERISCOPE-Opt: Machine learning-based prediction of optimal fermentation conditions and yields of recombinant periplasmic protein expressed in Escherichia coli.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun 3;20:2909-2920. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.006. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35765650 Free PMC article.
-
Glycation of Plant Proteins Via Maillard Reaction: Reaction Chemistry, Technofunctional Properties, and Potential Food Application.Foods. 2021 Feb 9;10(2):376. doi: 10.3390/foods10020376. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33572281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for the aminoacid composition of proteins from halophilic archea.PLoS Biol. 2009 Dec;7(12):e1000257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000257. Epub 2009 Dec 15. PLoS Biol. 2009. PMID: 20016684 Free PMC article.
-
Potential aggregation prone regions in biotherapeutics: A survey of commercial monoclonal antibodies.MAbs. 2009 May-Jun;1(3):254-67. doi: 10.4161/mabs.1.3.8035. Epub 2009 May 29. MAbs. 2009. PMID: 20065649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ries-Kautt M, Ducruix A. Inferences drawn from physicochemical studies of crystallogenesis and precrystalline state. Methods Enzymol. 1997;276:23–59. - PubMed
-
- Bagby S, Tong KI, Ikura M. Optimization of protein solubility and stability for protein nuclear magnetic resonance. Methods Enzymol. 2001;339:20–41. - PubMed
-
- Frank S, Kammerer RA, Hellstern S, Pegoraro S, Stetefeld J, Lustig A, Moroder L, Engel J. Toward a high-resolution structure of phospholamban: design of soluble transmembrane domain mutants. Biochemistry. 2000;39:6825–6831. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Cocco MJ, Steitz TA, Engelman DM. Conversion of phospholamban into a soluble pentameric helical bundle. Biochemistry. 2001;40:6636–6645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

