A Bir1-Sli15 complex connects centromeres to microtubules and is required to sense kinetochore tension
- PMID: 17174893
- PMCID: PMC2265205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.049
A Bir1-Sli15 complex connects centromeres to microtubules and is required to sense kinetochore tension
Abstract
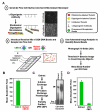
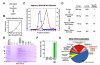
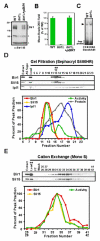
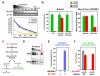
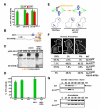
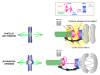
Proper connections between centromeres and spindle microtubules are of critical importance in ensuring accurate segregation of the genome during cell division. Using an in vitro approach based on the sequence-specific budding yeast centromere, we identified a complex of the chromosomal passenger proteins Bir1 and Sli15 (Survivin and INCENP) that links centromeres to microtubules. This linkage does not require Ipl1/Aurora B kinase, whose targeting and activation are controlled by Bir1 and Sli15. Ipl1 is the tension-dependent regulator of centromere-microtubule interactions that ensures chromosome biorientation on the spindle. Elimination of the linkage between centromeres and microtubules mediated by Bir1-Sli15 phenocopies mutations that selectively cripple Ipl1 kinase activation. These findings lead us to propose that the Bir1-Sli15-mediated linkage, which bridges centromeres and microtubules and includes the Aurora kinase-activating domain of INCENP family proteins, is the tension sensor that relays the mechanical state of centromere-microtubule attachments into local control of Ipl1 kinase activity.
Figures
References
-
- Adams RR, Wheatley SP, Gouldsworthy AM, Kandels-Lewis SE, Carmena M, Smythe C, Gerloff DL, Earnshaw WC. INCENP binds the Aurora-related kinase AIRK2 and is required to target it to chromosomes, the central spindle and cleavage furrow. Curr Biol. 2000;10:1075–1078. - PubMed
-
- Andrews PD, Knatko E, Moore WJ, Swedlow JR. Mitotic mechanics: the auroras come into view. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:672–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

