The histone gene transcription factor HiNF-P stabilizes its cell cycle regulatory co-activator p220NPAT
- PMID: 17176114
- PMCID: PMC2597183
- DOI: 10.1021/bi061425m
The histone gene transcription factor HiNF-P stabilizes its cell cycle regulatory co-activator p220NPAT
Abstract
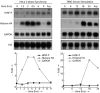
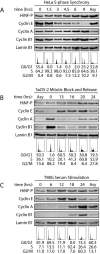
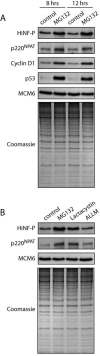
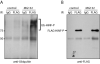
Orderly progression through the cell cycle requires the transcriptional activation of histone genes to support packaging of newly replicated DNA. Induction of human histone gene expression is mediated by a co-activation complex containing transcription factor HiNF-P and its cofactor p220NPAT. Here, using cells synchronized in S-phase and in mitosis, as well as serum-stimulated cells, we have investigated how HiNF-P is regulated during the cell cycle and examined its stability relative to p220NPAT. We find that while HiNF-P is maintained at steady-state levels throughout the cell cycle, both HiNF-P and p220NPAT are actively degraded by the proteasome pathway. Importantly, elevation of HiNF-P levels enhances the stability of its co-activator p220NPAT. The HiNF-P-dependent stabilization of p220NPAT may reinforce signaling through the cyclin E/CDK2/p220NPAT pathway and contribute to coordinate control of histone gene expression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CDK inhibitors selectively diminish cell cycle controlled activation of the histone H4 gene promoter by p220NPAT and HiNF-P.J Cell Physiol. 2009 May;219(2):438-48. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21687. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19170105 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional activation of the histone nuclear factor P (HiNF-P) gene by HiNF-P and its cyclin E/CDK2 responsive co-factor p220NPAT defines a novel autoregulatory loop at the G1/S phase transition.Gene. 2007 Nov 1;402(1-2):94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.07.027. Epub 2007 Aug 9. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17826007 Free PMC article.
-
HiNF-P directly links the cyclin E/CDK2/p220NPAT pathway to histone H4 gene regulation at the G1/S phase cell cycle transition.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;25(14):6140-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.14.6140-6153.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15988025 Free PMC article.
-
Modifications in molecular mechanisms associated with control of cell cycle regulated human histone gene expression during differentiation.Cell Biophys. 1989 Dec;15(3):201-23. doi: 10.1007/BF02989684. Cell Biophys. 1989. PMID: 2480181 Review.
-
Cell cycle dependent phosphorylation and subnuclear organization of the histone gene regulator p220(NPAT) in human embryonic stem cells.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Oct;213(1):9-17. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21119. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17520687 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic control of cell cycle-dependent histone gene expression is a principal component of the abbreviated pluripotent cell cycle.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;32(19):3860-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00736-12. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22826438 Free PMC article.
-
CDK inhibitors selectively diminish cell cycle controlled activation of the histone H4 gene promoter by p220NPAT and HiNF-P.J Cell Physiol. 2009 May;219(2):438-48. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21687. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19170105 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic-Mediated Regulation of Gene Expression for Biological Control and Cancer: Cell and Tissue Structure, Function, and Phenotype.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2022;70:339-373. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-06573-6_12. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2022. PMID: 36348114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of Heat Shock Protein Cpn10 with the Cyclin E/Cdk2 Substrate Nuclear Protein Ataxia-Telangiectasia (NPAT) Is Involved in Regulating Histone Transcription.J Biol Chem. 2015 Dec 4;290(49):29290-300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.659201. Epub 2015 Oct 1. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26429916 Free PMC article.
-
Fidelity of histone gene regulation is obligatory for genome replication and stability.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jul;34(14):2650-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01567-13. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24797072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holmes WF, Braastad CD, Mitra P, Hampe C, Doenecke D, Albig W, Stein JL, van Wijnen AJ, Stein GS. Coordinate control and selective expression of the full complement of replication-dependent histone H4 genes in normal and cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:37400–37407. - PubMed
-
- van der Meijden CMJ, Vaughan PS, Staal A, Albig W, Doenecke D, Stein JL, Stein GS, van Wijnen AJ. Selective expression of specific histone H4 genes reflects distinctions in transcription factor interactions with divergent H4 promoter elements. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998;1442:82–100. - PubMed
-
- Lichtler AC, Sierra F, Clark S, Wells JR, Stein JL, Stein GS. Multiple H4 histone mRNAs of HeLa cells are encoded in different genes. Nature. 1982;298:195–198. - PubMed
-
- Trappe R, Doenecke D, Albig W. The expression of human H2A-H2B histone gene pairs is regulated by multiple sequence elements in their joint promoters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1999;1446:341–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

