Efficacy in treatment of cervical HRHPV infection by combination of beta interferon, and herbal therapy in woman with different cervical lesions
- PMID: 17177657
- PMCID: PMC5807977
- DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2006.3128
Efficacy in treatment of cervical HRHPV infection by combination of beta interferon, and herbal therapy in woman with different cervical lesions
Abstract
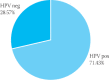
Cervical dysplasia, a premalignant lesion that can progress to cervical cancer, is caused primarily by a sexually transmitted infection with an oncogenic strain of the human papillomavirus (HPV). The HPV infections are treated through destroying the clinical lesions: laser, cryotherapy, podophyllin... The hope is that by causing local tissue inflammation that the body will be stimulated to mount an antibody response and thereby prevent recurrence. In contrast to other prevention approaches, vaccines can reduce susceptibility in uninfected partners by stimulating the immune system. Aloe vera has also been reported to retard tumour growth and stimulate the immune response to viruses. A list of possible actions of propolis includes: antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, antithrombotic and immunomodulatory. Research on the possible role of some B vitamins in preventing cancer began in the last few decades, but however this complex have an influence on immune status. The aim of our study is to try to treat the HPV infection as confirmed cause of neoplastic transformation with some herbal therapy and interferon and to try define the guidelines in the management of the HPV positive patients. Goal of this paper is to search for evidence of efficacy of any treatment for HPV infection of the cervix mostly in woman with no concomitant CIN. Fifty five woman affected by HPV genital infection were enrolled in the study from September 2005 to April 2006. Patients were classified according to the results of the HPV testing prior and after the therapy. Patients were randomized into two groups: the first group was HPV positive woman treated with other than recommended therapy (n=20), (control group); the second group was pharmacologically treated with intravaginal administration of an interferon and aloe vera-propolis in recommended scheme (n=35) with treatment of the possible fungal or bacterial genital infection prior to the specific therapy. The almost same therapy was recommended to the male partner. Patients from the second group used B complex during the therapy. Patients were retested for the HPV presence after three or six month from therapy depend of the presence bacterial or fungal genital coinfection. Three months after applied therapy HPV infection was still present in more than 90% of the patients in the first group. In the second group treated according to the recommended therapy scheme HPV infection disappeared in 71.42% of the patients after three months and in 100% of patients after six months. Samples of the cervical smear for the HPV analysis were being taken during routine gynecological examinations, by using sticks with cotton, taken from the Digene Specimen Collection Kit, from the whole surface of a portion, and by mild rotating moves from the outer cervical entrance. Our results suggest that the combination of interferon and herbal therapy with B complex is effective, atraumatic and simple non-surgical treatment of HPV infection. Since prospective efficacy trials will take several years to complete, considering alternative approaches is also worthwhile.
Figures
References
-
- Marshall K. Cervical dysplasia: early intervention. Altern Med Rev. 2003;8(2):156–170. - PubMed
-
- Bosch FX, Munoz N, de Sanjose Human papillomavirus and other risk factors for cervical cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 1997;51(6-7):268–275. - PubMed
-
- Wierrani F, Kubin A, Jindra R, et al. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy of intraepithelial neoplasia and human papillomavirus of the uterine cervix – A new experimental approach. Cancer Detection & Prevention. 1999;23(4):351–355. - PubMed
-
- Parent D, Binet H. Viral sexually transmitted diseases and their treatments. Rev. Med. Brux. 1998;19(4):A 185–190. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous