The role of synovial macrophages and macrophage-produced cytokines in driving aggrecanases, matrix metalloproteinases, and other destructive and inflammatory responses in osteoarthritis
- PMID: 17177994
- PMCID: PMC1794533
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2099
The role of synovial macrophages and macrophage-produced cytokines in driving aggrecanases, matrix metalloproteinases, and other destructive and inflammatory responses in osteoarthritis
Abstract
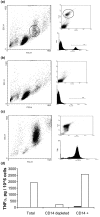
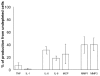
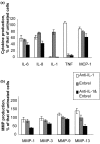
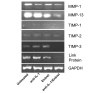
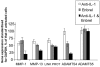
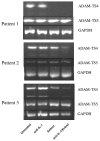
There is an increasing body of evidence that synovitis plays a role in the progression of osteoarthritis and that overproduction of cytokines and growth factors from the inflamed synovium can influence the production of degradative enzymes and the destruction of cartilage. In this study, we investigate the role of synovial macrophages and their main proinflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), in driving osteoarthritis synovitis and influencing the production of other pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, production of matrix metalloproteinases, and expression of aggrecanases in the osteoarthritis synovium. We established a model of cultures of synovial cells from digested osteoarthritis synovium derived from patients undergoing knee or hip arthroplasties. By means of anti-CD14-conjugated magnetic beads, specific depletion of osteoarthritis synovial macrophages from these cultures could be achieved. The CD14+-depleted cultures no longer produced significant amounts of macrophage-derived cytokines like IL-1 and TNF-alpha. Interestingly, there was also significant downregulation of several cytokines, such as IL-6 and IL-8 (p < 0.001) and matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 3 (p < 0.01), produced chiefly by synovial fibroblasts. To investigate the mechanisms involved, we went on to use specific downregulation of IL-1 and/or TNF-alpha in these osteoarthritis cultures of synovial cells. The results indicated that neutralisation of both IL-1 and TNF-alpha was needed to achieve a degree of cytokine (IL-6, IL-8, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1) and matrix metalloproteinase (1, 3, 9, and 13) inhibition, as assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), similar to that observed in CD14+-depleted cultures. Another interesting observation was that in these osteoarthritis cultures of synovial cells, IL-1beta production was independent of TNF-alpha, in contrast to the situation in rheumatoid arthritis. Using RT-PCR, we also demonstrated that whereas the ADAMTS4 (a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin motifs 4) aggrecanase was driven mainly by TNF-alpha, ADAMTS5 was not affected by neutralisation of IL-1 and/or TNF-alpha. These results suggest that, in the osteoarthritis synovium, both inflammatory and destructive responses are dependent largely on macrophages and that these effects are cytokine-driven through a combination of IL-1 and TNF-alpha.
Figures

References
-
- Clark AG, Jordan JM, Vilim V, Renner JB, Dragomir AD, Luta G, Kraus VB. Serum cartilage oligomeric protein reflects osteoarthritis presence and severity: the Johnston County Osteoarthritis Project. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:2356–2364. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199911)42:11<2356::AID-ANR14>3.0.CO;2-R. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

