Cholinergic modulation of Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats: differential effects of intrahippocampal infusion of mecamylamine and methyllycaconitine
- PMID: 17178240
- PMCID: PMC1951534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2006.11.001
Cholinergic modulation of Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats: differential effects of intrahippocampal infusion of mecamylamine and methyllycaconitine
Abstract
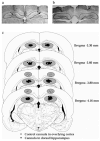
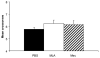
The cholinergic system has consistently been implicated in Pavlovian fear conditioning. Considerable work has been done to localize specific nicotinic receptor subtypes in the hippocampus and determine their functional importance; however, the specific function of many of these subtypes has yet to be determined. An alpha7 nicotinic antagonist methyllycaconitine (MLA) (35 microg), and a broad spectrum non-alpha7 nicotinic antagonist mecamylamine (35 microg) was injected directly into the dorsal hippocampus or overlying cortex either 15 min pre-, 1 min post-, or 6h post-fear conditioning. One week after conditioning, retention of contextual and cue (tone) conditioning were assessed. A significant impairment in retention of contextual fear was observed when mecamylamine was injected 15 min pre- and 1 min post-conditioning. No significant impairment was observed when mecamylamine was injected 6h post-conditioning. Likewise, a significant impairment in retention of contextual fear was observed when MLA was injected 1 min post-conditioning; however, in contrast, MLA did not show any significant impairments when injected 15 min pre-conditioning, but did show a significant impairment when injected 6h post-conditioning. There were no significant impairments observed when either drug was injected into overlying cortex. No significant impairments were observed in cue conditioning for either drug. In general, specific temporal dynamics involved in nicotinic receptor function were found relative to time of receptor dysfunction. The results indicate that the greatest deficits in long-term retention (1 week) of contextual fear are produced by central infusion of MLA minutes to hours post-conditioning or mecamylamine within minutes of conditioning.
Figures
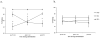
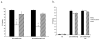
Similar articles
-
The role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in trace fear conditioning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010 Oct;94(3):353-63. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.08.001. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010. PMID: 20727979 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor involvement in the enhancing effect of acute nicotine on contextual fear conditioning.J Neurosci. 2007 Oct 3;27(40):10870-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3242-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17913920 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of DHBE and MLA on nicotine-induced enhancement of contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006 Mar;184(3-4):345-52. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0047-y. Epub 2005 Jun 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006. PMID: 15988571
-
Cholinergic modulation of pavlovian fear conditioning: effects of intrahippocampal scopolamine infusion.Hippocampus. 2001;11(4):371-6. doi: 10.1002/hipo.1051. Hippocampus. 2001. PMID: 11530841
-
Involvement of alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic receptors in long-term memory formation in the honeybee (Apis mellifera).Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2006 Sep;86(2):164-74. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2006.02.003. Epub 2006 Apr 17. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2006. PMID: 16616529
Cited by
-
Cellular, molecular, and genetic substrates underlying the impact of nicotine on learning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Jan;107:108-32. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 23973448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid beta mediates memory formation.Learn Mem. 2009 Mar 24;16(4):267-72. doi: 10.1101/lm.1310209. Print 2009 Apr. Learn Mem. 2009. PMID: 19318468 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic acetylcholine induces sharp wave ripples in the basolateral amygdala through nicotinic receptors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 2:2024.12.01.626291. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.01.626291. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39677685 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Nicotinic modulation of descending pain control circuitry.Pain. 2017 Oct;158(10):1938-1950. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000993. Pain. 2017. PMID: 28817416 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic regulation of fear learning and extinction.J Neurosci Res. 2017 Mar;95(3):836-852. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23840. Epub 2016 Oct 5. J Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 27704595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams CE, Stitzel JA, Collins AC, Freedman R. Alpha7-nicotinic receptor expression and the anatomical organization of hippocampal interneurons. Brain Research. 2001;922:180–190. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. I. Pharmacological and functional evidence for distinct structural subtypes. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1993;265:1455–1473. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Maren S, Fanselow MS. Scopolamine selectively disrupts the acquisition of contextual fear conditioning in rats. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. 1995;64:191–194. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Maren S, Sage JR, Goodrich S, Fanselow MS. Scopolamine and Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats: dose-effect analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999b;21:731–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

