Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular biology and therapy
- PMID: 17178294
- PMCID: PMC1861815
- DOI: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.10.015
Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular biology and therapy
Abstract
Advanced and metastatic hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) are challenging to treat, and no cytotoxic agents have impacted survival. The underlying liver cirrhosis that commonly accompanies HCC provides an additional challenge; indeed, functional scoring of cirrhosis and HCC is a critical component of patient evaluation. Currently, the molecular biology and pathogenesis of HCC are being increasingly investigated, which may lead to better understanding of the evolution of the disease, especially differing etiologies and identification of survival genes that may affect outcome. Early studies of targeted therapies in HCC have shown disease stabilization, and an increased understanding of the mechanism(s) of these novel agents combined with correlative studies may lead to the identification of an active agent or combination of agents that impacts the natural history of HCC.
Figures


References
-
- McGlynn KA, Tsao L, Hsing AW, et al. International trends and patterns of primary liver cancer. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:290–6. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Mason AC. Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. New Engl J Med. 1999;340:745–50. - PubMed
-
- Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–9. - PubMed
-
- Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. In: Child CG, editor. The liver and portal hypertension. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 1964. pp. 50–64.
-
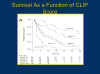
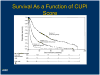
- A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma. A retrospective study of 435 patients. The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) Hepatology. 1998;28:751–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

