Staufen- and FMRP-containing neuronal RNPs are structurally and functionally related to somatic P bodies
- PMID: 17178403
- PMCID: PMC1955741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.10.028
Staufen- and FMRP-containing neuronal RNPs are structurally and functionally related to somatic P bodies
Abstract
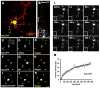
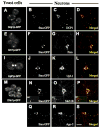
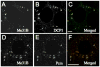
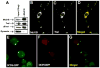
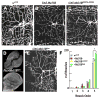
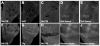
Local control of mRNA translation modulates neuronal development, synaptic plasticity, and memory formation. A poorly understood aspect of this control is the role and composition of ribonucleoprotein (RNP) particles that mediate transport and translation of neuronal RNAs. Here, we show that staufen- and FMRP-containing RNPs in Drosophila neurons contain proteins also present in somatic "P bodies," including the RNA-degradative enzymes Dcp1p and Xrn1p/Pacman and crucial components of miRNA (argonaute), NMD (Upf1p), and general translational repression (Dhh1p/Me31B) pathways. Drosophila Me31B is shown to participate (1) with an FMRP-associated, P body protein (Scd6p/trailer hitch) in FMRP-driven, argonaute-dependent translational repression in developing eye imaginal discs; (2) in dendritic elaboration of larval sensory neurons; and (3) in bantam miRNA-mediated translational repression in wing imaginal discs. These results argue for a conserved mechanism of translational control critical to neuronal function and open up new experimental avenues for understanding the regulation of mRNA function within neurons.
Figures

References
-
- Antar LN, Dictenberg JB, Plociniak M, Afroz R, Bassell GJ. Localization of FMRP-associated mRNA granules and requirement of microtubules for activity-dependent trafficking in hippocampal neurons. Genes Brain Behav. 2005;4:350–359. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf SI, McLoon AL, Sclarsic SM, Kunes S. Synaptic protein synthesis associated with memory is regulated by the RISC pathway in Drosophila. Cell. 2006;124:191–205. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya SN, Habermacher R, Martine U, Closs EI, Fillipowicz W. Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell. 2006;125:1111–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

