c-Fos-deficient mice are susceptible to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection
- PMID: 17178788
- PMCID: PMC1828558
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01316-06
c-Fos-deficient mice are susceptible to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection
Abstract
c-Fos is a component of transcription factor AP-1. We show that macrophages lacking c-Fos exhibit enhanced production of proinflammatory cytokines, potentiated NF-kappaB phosphorylation, and increased cell death following Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection. Furthermore, mice lacking c-Fos are highly susceptible to infection, suggesting that c-Fos confers resistance to Salmonella infection in mice.
Figures
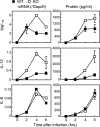


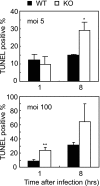
 , P < 0.05 versus wild-type control;
, P < 0.05 versus wild-type control; 
 , P < 0.01 versus wild-type control.
, P < 0.01 versus wild-type control.
 , P < 0.05 versus wild-type control;
, P < 0.05 versus wild-type control; 
 , P < 0.01 versus wild-type control. Cont., control; Infec., infected. (C) Survival of mice was monitored for 1 week after infection as described for panel A. n = 4 for each genotype.
, P < 0.01 versus wild-type control. Cont., control; Infec., infected. (C) Survival of mice was monitored for 1 week after infection as described for panel A. n = 4 for each genotype.References
-
- Aderem, A., and R. J. Ulevitch. 2000. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 406:782-787. - PubMed
-
- Dillon, S., A. Agrawal, T. Van Dyke, G. Landreth, L. McCauley, A. Koh, C. Maliszewski, S. Akira, and B. Pulendran. 2004. A Toll-like receptor 2 ligand stimulates Th2 responses in vivo, via induction of extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Fos in dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 172:4733-4743. - PubMed
-
- Grigoriadis, A. E., Z. Q. Wang, M. G. Cecchini, W. Hofstetter, R. Felix, H. A. Fleisch, and E. F. Wagner. 1994. c-Fos: a key regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone remodeling. Science 266:443-448. - PubMed
-
- Hueffer, K., and J. E. Galán. 2004. Salmonella-induced macrophage death: multiple mechanisms, different outcomes. Cell. Microbiol. 6:1019-1025. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

