Role of RpoS in fine-tuning the synthesis of Vi capsular polysaccharide in Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi
- PMID: 17178790
- PMCID: PMC1828562
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00888-06
Role of RpoS in fine-tuning the synthesis of Vi capsular polysaccharide in Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi
Abstract
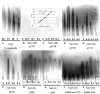
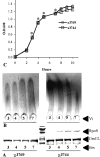
Regulation of the synthesis of Vi polysaccharide, a major virulence determinant in Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi, is under the control of two regulatory systems, ompR-envZ and rscB-rscC, which respond to changes in osmolarity. Some serotype Typhi strains exhibit overexpression of Vi polysaccharide, which masks clinical detection of lipopolysaccharide O antigen. This variation in Vi polysaccharide and O antigen display (VW variation) has been observed since the initial studies of serotype Typhi. In this study, we report that rpoS plays a role in this increased expression in Vi polysaccharide. We constructed a variety of isogenic serotype Typhi mutants that differed in their expression levels of RpoS and examined the role of the rpoS product in synthesis of Vi polysaccharide under different osmolarity conditions. Vi polysaccharide synthesis was also examined in serotype Typhi mutants in which the native promoter of the rpoS was replaced by an araCP(BAD) cassette, so that the expression of rpoS was arabinose dependent. The RpoS(-) strains showed increased syntheses of Vi polysaccharide, which at low and medium osmolarities masked O antigen detection. In contrast, RpoS(+) strains showed lower syntheses of Vi polysaccharide, and an increased detection of O antigen was observed. During exponential growth, when rpoS is unstable or present at low levels, serotype Typhi RpoS(+) strains overexpress the Vi polysaccharide at levels comparable to those for RpoS(-) strains. Our results show that RpoS is another regulator of Vi polysaccharide synthesis and contributes to VW variation in serotype Typhi, which has implications for the development of recombinant attenuated Salmonella vaccines in humans.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Regulation of Vi capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2008 Dec 1;2(6):412-20. doi: 10.3855/jidc.154. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2008. PMID: 19745516 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal Regulation of OmpR and Hfq and Their Regulatory Actions on the Vi Polysaccharide Capsular Antigen in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi.Curr Microbiol. 2018 Jun;75(6):773-778. doi: 10.1007/s00284-018-1447-7. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Curr Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29417203
-
Loss of very-long O-antigen chains optimizes capsule-mediated immune evasion by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.mBio. 2013 Jul 16;4(4):e00232-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00232-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 23860765 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Vi Negative Isolates of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhi.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1052:9-18. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7572-8_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29785477 Review.
-
Vi capsular polysaccharide: Synthesis, virulence, and application.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2017 Aug;43(4):440-452. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2016.1249335. Epub 2016 Nov 21. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27869515 Review.
Cited by
-
Salmonella Extracellular Polymeric Substances Modulate Innate Phagocyte Activity and Enhance Tolerance of Biofilm-Associated Bacteria to Oxidative Stress.Microorganisms. 2020 Feb 13;8(2):253. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8020253. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32070067 Free PMC article.
-
Role of cold shock proteins B and D in Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida physiology and virulence in lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus).Infect Immun. 2024 Aug 13;92(8):e0001124. doi: 10.1128/iai.00011-24. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 38920386 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella Biofilms Tolerate Hydrogen Peroxide by a Combination of Extracellular Polymeric Substance Barrier Function and Catalase Enzymes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 May 19;11:683081. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.683081. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34095002 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A are avirulent in newborn and infant mice even when expressing virulence plasmid genes of Salmonella Typhimurium.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2010 Nov 24;4(11):723-31. doi: 10.3855/jidc.1218. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2010. PMID: 21252450 Free PMC article.
-
A sopB deletion mutation enhances the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a heterologous antigen delivered by live attenuated Salmonella enterica vaccines.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):5238-46. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00720-08. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18765737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arricau, N., D. Hermant, H. Waxin, C. Ecobichon, P. S. Duffey, and M. Y. Popoff. 1998. The RcsB-RcsC regulatory system of Salmonella typhi differentially modulates the expression of invasion proteins, flagellin and Vi antigen in response to osmolarity. Mol. Microbiol. 29:835-850. - PubMed
-
- Black, R. E., M. M. Levine, M. L. Clements, G. Losonsky, D. Herrington, S. Berman, and S. B. Formal. 1987. Prevention of shigellosis by a Salmonella typhi-Shigella sonnei bivalent vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 155:1260-1265. - PubMed
-
- Coynault, C., and F. Norel. 1999. Comparison of the abilities of Salmonella typhimurium rpoS, aroA and rpoS aroA strains to elicit humoral immune responses in BALB/c mice and to cause lethal infection in athymic BALB/c mice. Microb. Pathog. 26:299-305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

