Deciphering the cross talk between hnRNP K and c-Src: the c-Src activation domain in hnRNP K is distinct from a second interaction site
- PMID: 17178840
- PMCID: PMC1820454
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02014-06
Deciphering the cross talk between hnRNP K and c-Src: the c-Src activation domain in hnRNP K is distinct from a second interaction site
Abstract
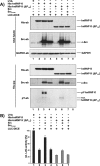
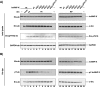
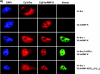
The protein tyrosine kinase c-Src is regulated by two intramolecular interactions. The repressed state is achieved through the interaction of the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain with the phosphorylated C-terminal tail and the association of the SH3 domain with a polyproline type II helix formed by the linker region between SH2 and the kinase domain. hnRNP K, the founding member of the KH domain protein family, is involved in chromatin remodeling, regulation of transcription, and translation of specific mRNAs and is a target in different signal transduction pathways. In particular, it functions as a specific activator and a substrate of the tyrosine kinase c-Src. Here we address the question how hnRNP K interacts with and activates c-Src. We define the proline residues in hnRNP K in the proline-rich motifs P2 (amino acids [aa] 285 to 297) and P3 (aa 303 to 318), which are necessary and sufficient for the specific activation of c-Src, and we dissect the amino acid sequence (aa 216 to 226) of hnRNP K that mediates a second interaction with c-Src. Our findings indicate that the interaction with c-Src and the activation of the kinase are separable functions of hnRNP K. hnRNP K acts as a scaffold protein that integrates signaling cascades by facilitating the cross talk between kinases and factors that mediate nucleic acid-directed processes.
Figures






References
-
- Alexandropoulos, K., and D. Baltimore. 1996. Coordinate activation of c-Src by SH3- and SH2-binding sites on a novel, p130 Cas-related protein, Sin. Genes Dev. 10:1341-1355. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, G., M. Koegl, N. Mazurenko, and S. A. Courtneidge. 1995. Sequence requirements for binding of Src family tyrosine kinases to activated growth factor receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 270:9840-9848. - PubMed
-
- Ball, L. J., R. Kuhne, J. Schneider-Mergener, and H. Oschkinat. 2005. Recognition of proline-rich motifs by protein-protein-interaction domains. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 44:2852-2869. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. T., and J. A. Cooper. 1996. Regulation, substrates and functions of Src. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1287:121-149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
