Type IV procollagen missense mutations associated with defects of the eye, vascular stability, the brain, kidney function and embryonic or postnatal viability in the mouse, Mus musculus: an extension of the Col4a1 allelic series and the identification of the first two Col4a2 mutant alleles
- PMID: 17179069
- PMCID: PMC1800636
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.064733
Type IV procollagen missense mutations associated with defects of the eye, vascular stability, the brain, kidney function and embryonic or postnatal viability in the mouse, Mus musculus: an extension of the Col4a1 allelic series and the identification of the first two Col4a2 mutant alleles
Abstract
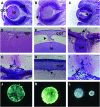
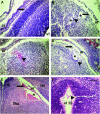
The basement membrane is important for proper tissue development, stability, and physiology. Major components of the basement membrane include laminins and type IV collagens. The type IV procollagens Col4a1 and Col4a2 form the heterotrimer [alpha1(IV)]2[alpha2(IV)], which is ubiquitously expressed in basement membranes during early developmental stages. We present the genetic, molecular, and phenotypic characterization of nine Col4a1 and three Col4a2 missense mutations recovered in random mutagenesis experiments in the mouse. Heterozygous carriers express defects in the eye, the brain, kidney function, vascular stability, and viability. Homozygotes do not survive beyond the second trimester. Ten mutations result in amino acid substitutions at nine conserved Gly sites within the collagenous domain, one mutation is in the carboxy-terminal noncollagenous domain, and one mutation is in the signal peptide sequence and is predicted to disrupt the signal peptide cleavage site. Patients with COL4A2 mutations have still not been identified. We suggest that the spontaneous intraorbital hemorrhages observed in the mouse are a clinically relevant phenotype with a relatively high predictive value to identify carriers of COL4A1 or COL4A2 mutations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Allelic heterogeneity contributes to variability in ocular dysgenesis, myopathy and brain malformations caused by Col4a1 and Col4a2 mutations.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Apr 1;23(7):1709-22. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt560. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24203695 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant mutations of Col4a1 result in basement membrane defects which lead to anterior segment dysgenesis and glomerulopathy.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Nov 1;14(21):3161-8. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi348. Epub 2005 Sep 13. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 16159887
-
Molecular and Genetic Analyses of Collagen Type IV Mutant Mouse Models of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage Identify Mechanisms for Stroke Prevention.Circulation. 2015 May 5;131(18):1555-65. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013395. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 25753534 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding phenotype of COL4A1 and COL4A2 mutations: clinical data on 13 newly identified families and a review of the literature.Genet Med. 2015 Nov;17(11):843-53. doi: 10.1038/gim.2014.210. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Genet Med. 2015. PMID: 25719457 Review.
-
Role of COL4A1 in basement-membrane integrity and cerebral small-vessel disease. The COL4A1 stroke syndrome.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(13):1317-24. doi: 10.2174/092986710790936293. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20166936 Review.
Cited by
-
Common somatic alterations identified in maffucci syndrome by molecular karyotyping.Mol Syndromol. 2014 Dec;5(6):259-67. doi: 10.1159/000365898. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Mol Syndromol. 2014. PMID: 25565925 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular matrix downregulation in the Drosophila heart preserves contractile function and improves lifespan.Matrix Biol. 2017 Oct;62:15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.10.008. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 27793636 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of a Novel B3GLCT Variant to Peters Plus Syndrome Discovered by a Combination of Next-Generation Sequencing and Automated Text Mining.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 28;20(23):6006. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236006. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31795264 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Chromatin-Remodeling Enzymes Regulate the Production of Critical ECM Components During Murine Lung Development.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Aug;44(8):1784-1798. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.320881. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38868942 Free PMC article.
-
Basement membranes' role in immune cell recruitment to the central nervous system.J Inflamm (Lond). 2024 Dec 20;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12950-024-00426-6. J Inflamm (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39707430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anker, M. C., J. Arnemann, K. Neumann, P. Ahrens, H. Schmidt et al., 2003. Alport syndrome with diffuse leiomyomatosis. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 119: 381–385. - PubMed
-
- Badenas, C., M. Praga, B. Tazón, L. Heidet, C. Arrondel et al., 2002. Mutations in the COL4A4 and COL4A3 genes cause familial benign hematuria. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13: 1248–1254. - PubMed
-
- Bell, S. E., A. Mavila, R. Salazar, K. J. Bayless, S. Kanagala et al., 2001. Differential gene expression during capillary morphogenesis in 3D collagen matrices: regulated expression of genes involved in basement membrane matrix assembly, cell cycle progression, cellular differentiation and G-protein signaling. J. Cell Sci. 114: 2755–2773. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen, J. D., H. Nielsen, G. von Heijne and S. Brunak, 2004. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 340: 783–795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

