Contribution of Trf4/5 and the nuclear exosome to genome stability through regulation of histone mRNA levels in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 17179095
- PMCID: PMC1840065
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.065987
Contribution of Trf4/5 and the nuclear exosome to genome stability through regulation of histone mRNA levels in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
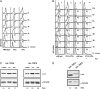
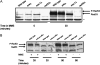
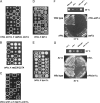
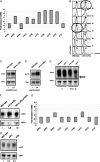
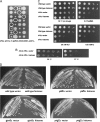
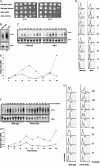
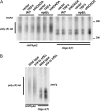
Balanced levels of histones are crucial for chromosome stability, and one major component of this control regulates histone mRNA amounts. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae poly(A) polymerases Trf4 and Trf5 are involved in a quality control mechanism that mediates polyadenylation and consequent degradation of various RNA species by the nuclear exosome. None of the known RNA targets, however, explains the fact that trf mutants have specific cell cycle defects consistent with a role in maintaining genome stability. Here, we investigate the role of Trf4/5 in regulation of histone mRNA levels. We show that loss of Trf4 and Trf5, or of Rrp6, a component of the nuclear exosome, results in elevated levels of transcripts encoding DNA replication-dependent histones. Suggesting that increased histone levels account for the phenotypes of trf mutants, we find that TRF4 shows synthetic genetic interactions with genes that negatively regulate histone levels, including RAD53. Moreover, synthetic lethality of trf4Delta rad53Delta is rescued by reducing histone levels whereas overproduction of histones is deleterious to trf's and rrp6Delta mutants. These results identify TRF4, TRF5, and RRP6 as new players in the regulation of histone mRNA levels in yeast. To our knowledge, the histone transcripts are the first mRNAs that are upregulated in Trf mutants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Distinct roles of non-canonical poly(A) polymerases in RNA metabolism.PLoS Genet. 2009 Jul;5(7):e1000555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000555. Epub 2009 Jul 10. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19593367 Free PMC article.
-
Trf4 and Trf5 proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae exhibit poly(A) RNA polymerase activity but no DNA polymerase activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;25(22):10183-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.22.10183-10189.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16260630 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the nuclear exosome component RRP6 leads to continued accumulation of the histone mRNA HTB1 in S-phase of the cell cycle in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(18):6268-79. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm691. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17855393 Free PMC article.
-
Rrp6: Integrated roles in nuclear RNA metabolism and transcription termination.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Jan-Feb;7(1):91-104. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1317. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 26612606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of histone gene transcription in yeast.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Feb;71(4):599-613. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1443-9. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 23974242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A family of poly(U) polymerases.RNA. 2007 Jun;13(6):860-7. doi: 10.1261/rna.514007. Epub 2007 Apr 20. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17449726 Free PMC article.
-
New ways to meet your (3') end oligouridylation as a step on the path to destruction.Genes Dev. 2008 Jan 1;22(1):1-7. doi: 10.1101/gad.1634508. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18172159 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
A transcriptome-wide atlas of RNP composition reveals diverse classes of mRNAs and lncRNAs.Cell. 2013 Aug 29;154(5):996-1009. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.047. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23993093 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the RNA helicase SKIV2L2 impairs mitotic progression and replication-dependent histone mRNA turnover in murine cell lines.RNA. 2017 Jun;23(6):910-926. doi: 10.1261/rna.060640.117. Epub 2017 Mar 28. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28351885 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation and functions of the nuclear RNA exosome complex.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Apr;17(4):227-39. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2015.15. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26726035 Review.
References
-
- Adkins, M. W., and J. K. Tyler, 2004. The histone chaperone Asf1p mediates global chromatin disassembly in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 52069–52074. - PubMed
-
- Barnard, D. C., K. Ryan, J. L. Manley and J. D. Richter, 2004. Symplekin and xGLD-2 are required for CPEB-mediated cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Cell 119: 641–651. - PubMed
-
- Begley, T. J., A. S. Rosenbach, T. Ideker and L. D. Samson, 2002. Damage recovery pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae revealed by genomic phenotyping and interactome mapping. Mol. Cancer Res. 1: 103–112. - PubMed
-
- Brownell, J. E., and C. D. Allis, 1996. Special HATs for special occasions: linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 6: 176–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

