Global eQTL mapping reveals the complex genetic architecture of transcript-level variation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17179097
- PMCID: PMC1840073
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.064972
Global eQTL mapping reveals the complex genetic architecture of transcript-level variation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
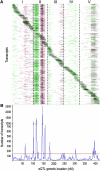
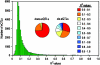
The genetic architecture of transcript-level variation is largely unknown. The genetic determinants of transcript-level variation were characterized in a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population (n = 211) of Arabidopsis thaliana using whole-genome microarray analysis and expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) mapping of transcript levels as expression traits (e-traits). Genetic control of transcription was highly complex: one-third of the quantitatively controlled transcripts/e-traits were regulated by cis-eQTL, and many trans-eQTL mapped to hotspots that regulated hundreds to thousands of e-traits. Several thousand eQTL of large phenotypic effect were detected, but almost all (93%) of the 36,871 eQTL were associated with small phenotypic effects (R(2) < 0.3). Many transcripts/e-traits were controlled by multiple eQTL with opposite allelic effects and exhibited higher heritability in the RILs than their parents, suggesting nonadditive genetic variation. To our knowledge, this is the first large-scale global eQTL study in a relatively large plant mapping population. It reveals that the genetic control of transcript level is highly variable and multifaceted and that this complexity may be a general characteristic of eukaryotes.
Figures
References
-
- Basten, C. J., B. S. Weir and Z.-B. Zeng, 1999. QTL Cartographer, Version 1.13. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC.
-
- Beavis, W. D., 1998. QTL analyses: power, precision, and accuracy, pp. 145–162 in Molecular Dissection of Complex Traits, edited by A. H. Paterson. CRC Press, Cleveland/Boca Raton, FL.
-
- Bogdan, M., and R. W. Doerge, 2005. Biased estimators of quantitative trait locus heritability and location in interval mapping. Heredity 95: 476–484. - PubMed
-
- Bolstad, B. M., R. A. Irizarry, M. Astrand and T. P. Speed, 2003. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19: 185–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

