Mutations in the connection domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase increase 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine resistance
- PMID: 17179211
- PMCID: PMC1765458
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609642104
Mutations in the connection domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase increase 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine resistance
Abstract
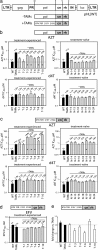
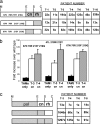
We previously proposed that a balance between nucleotide excision and template RNA degradation plays an important role in nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) resistance. To explore the predictions of this concept, we analyzed the role of patient-derived C-terminal domains of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) in NRTI resistance. We found that when the polymerase domain contained previously described thymidine analog resistance mutations, mutations in the connection domain increased resistance to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) from 11-fold to as much as 536-fold over wild-type RT. Mutational analysis showed that amino acid substitutions E312Q, G335C/D, N348I, A360I/V, V365I, and A376S were associated strongly with the observed increase in AZT resistance; several of these mutations also decreased RT template switching, suggesting that they alter the predicted balance between nucleotide excision and template RNA degradation. These results indicate that mutations in the C-terminal domain of RT significantly enhance clinical NRTI resistance and should be considered in genotypic and phenotypic drug resistance studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

