FAIRE (Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements) isolates active regulatory elements from human chromatin
- PMID: 17179217
- PMCID: PMC1891346
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.5533506
FAIRE (Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements) isolates active regulatory elements from human chromatin
Abstract
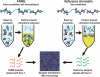
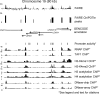
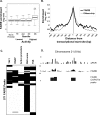
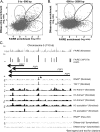
DNA segments that actively regulate transcription in vivo are typically characterized by eviction of nucleosomes from chromatin and are experimentally identified by their hypersensitivity to nucleases. Here we demonstrate a simple procedure for the isolation of nucleosome-depleted DNA from human chromatin, termed FAIRE (Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements). To perform FAIRE, chromatin is crosslinked with formaldehyde in vivo, sheared by sonication, and phenol-chloroform extracted. The DNA recovered in the aqueous phase is fluorescently labeled and hybridized to a DNA microarray. FAIRE performed in human cells strongly enriches DNA coincident with the location of DNaseI hypersensitive sites, transcriptional start sites, and active promoters. Evidence for cell-type-specific patterns of FAIRE enrichment is also presented. FAIRE has utility as a positive selection for genomic regions associated with regulatory activity, including regions traditionally detected by nuclease hypersensitivity assays.
Figures

References
-
- Alberts B., Johnson A., Lewis J., Raff M., Roberts K., Walter P., Johnson A., Lewis J., Raff M., Roberts K., Walter P., Lewis J., Raff M., Roberts K., Walter P., Raff M., Roberts K., Walter P., Roberts K., Walter P., Walter P. Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland Science; New York: 2002.
-
- Ashurst J.L., Chen C.K., Gilbert J.G., Jekosch K., Keenan S., Meidl P., Searle S.M., Stalker J., Storey R., Trevanion S., Chen C.K., Gilbert J.G., Jekosch K., Keenan S., Meidl P., Searle S.M., Stalker J., Storey R., Trevanion S., Gilbert J.G., Jekosch K., Keenan S., Meidl P., Searle S.M., Stalker J., Storey R., Trevanion S., Jekosch K., Keenan S., Meidl P., Searle S.M., Stalker J., Storey R., Trevanion S., Keenan S., Meidl P., Searle S.M., Stalker J., Storey R., Trevanion S., Meidl P., Searle S.M., Stalker J., Storey R., Trevanion S., Searle S.M., Stalker J., Storey R., Trevanion S., Stalker J., Storey R., Trevanion S., Storey R., Trevanion S., Trevanion S., et al. The Vertebrate Genome Annotation (Vega) database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:D459–D465. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y., Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Bernstein B.E., Liu C.L., Humphrey E.L., Perlstein E.O., Schreiber S.L., Liu C.L., Humphrey E.L., Perlstein E.O., Schreiber S.L., Humphrey E.L., Perlstein E.O., Schreiber S.L., Perlstein E.O., Schreiber S.L., Schreiber S.L. Global nucleosome occupancy in yeast. Genome Biol. 2004;5:R62. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boeger H., Griesenbeck J., Strattan J.S., Kornberg R.D., Griesenbeck J., Strattan J.S., Kornberg R.D., Strattan J.S., Kornberg R.D., Kornberg R.D. Nucleosomes unfold completely at a transcriptionally active promoter. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:1587–1598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
