Effects of bladder training and/or tolterodine in female patients with overactive bladder syndrome: a prospective, randomized study
- PMID: 17179687
- PMCID: PMC2721929
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.6.1060
Effects of bladder training and/or tolterodine in female patients with overactive bladder syndrome: a prospective, randomized study
Abstract
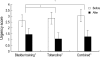
We compared the effects of bladder training and/or tolterodine as first line treatment in female patients with overactive bladder (OAB). One hundred and thirty-nine female patients with OAB were randomized to treatment with bladder training (BT), tolterodine (To, 2 mg twice daily) or both (Co) for 12 weeks. Treatment efficacy was measured by micturition diary, urgency scores and patients' subjective assessment of their bladder condition. Mean frequency and nocturia significantly decreased in all treatment groups, declining 25.9% and 56.1%, respectively, in the BT group; 30.2% and 65.4%, respectively, in the To group; and 33.5% and 66.3%, respectively in the Co group (p<0.05 for each). The decrease in frequency was significantly greater in the Co group than in the BT group (p<0.05). Mean urgency score decreased by 44.8%, 62.2% and 60.2% in the BT, To, and Co groups, respectively, and the improvement was significantly greater in the To and Co groups than in the BT group (p<0.05 for each). Although BT, To and their combination were all effective in controlling OAB symptoms, combination therapy was more effective than either method alone. Tolterodine alone may be instituted as a first-line therapy, but may be more effective when combined with bladder training.
Figures

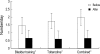
References
-
- Milsom I, Abrams P, Cardozo L, Roberts RG, Thuroff J, Wein AJ. How widespread are the symptoms of an overactive bladder and how are they managed? A population-based prevalence study. BJU Int. 2001;87:760–766. - PubMed
-
- Stewart WF, Van Rooyen JB, Cundiff GW, Abrams P, Herzog AR, Corey R, Hunt TL, Wein AJ. Prevalence and burden of overactive bladder in the United States. World J Urol. 2003;20:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Blok BF, Holstege G. The central control of micturition and continence: implications for urology. BJU Int. 1999;83:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Igawa Y. Discussion: functional role of M1, M2, and M3 muscarinic receptors in overactive bladder. Urology. 2000;55:47–50. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick JM. Facts and future lines of research in lower urinary tract symptoms in men and women: an overview of the role of α1-adrenoreceptor antagonists. BJU Int. 2000;85:1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

