The function of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors of the saphenous artery in caveolin-1 knockout and wild-type mice
- PMID: 17179950
- PMCID: PMC2013897
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706980
The function of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors of the saphenous artery in caveolin-1 knockout and wild-type mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: Adrenoceptors can associate with cardiac caveolae. To investigate the function of vascular caveolae, adrenoceptor-mediated effects were compared in the saphenous artery of caveolin-1 knockout (cav-1KO) and wild-type (WT) mice.
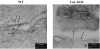
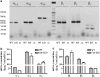
Experimental approach: Electronmicroscopy was used to detect caveolae. Real-Time quantitative PCR was used for adrenoceptor subtypes. Catecholamine-evoked contractions and relaxations were studied in arterial segments.
Key results: Caveolae were found in arterial smooth muscle from WT but not from cav-1KO mice. Arterial mRNA levels for the adrenoceptors alpha1A, alpha1B, alpha1D, beta1, beta2 and beta3 were similar in cav-1KO and WT. (-)-Noradrenaline contracted cav-1KO (-log EC50M=7.1) and WT (-log EC50M=7.3) arteries through prazosin-sensitive receptors. Maximum (-)-noradrenaline-evoked contractions were greater in cav-1KO than WT arteries. (-)-Isoprenaline relaxed WT arteries (-log EC50M=7.3) more potently than cav-1KO arteries (-log EC50M=6.8); the effects were antagonized partially and similarly by the beta2-selective antagonist ICI118551 (50 nM). The (-)-isoprenaline-evoked relaxation was partially antagonized by the beta1-adrenoceptor-selective antagonist CGP20712 (300 nM) in WT but not cav-1KO arteries. The beta3-adrenoceptor-selective antagonist L748337 (100 nM) partially antagonized the relaxant effects of (-)-isoprenaline in cav-1KO but not in WT arteries. BRL37344 partially relaxed arteries through beta3-adrenoceptors in cav-1KO but not WT. The relaxant effects of BRL37344 were decreased by the NO synthase inhibitor OmegaL-nitroarginine.
Conclusions and implications: The function of arterial alpha1- and beta2-adrenoceptors is similar in cav-1KO and WT mice. beta1-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation in WT is lost in cav-1KO and replaced by the appearance of beta3-adrenoceptors.
Figures




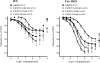


Comment in
-
Do studies in caveolin-knockouts teach us about physiology and pharmacology or instead, the ways mice compensate for 'lost proteins'?Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Feb;150(3):251-4. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706981. Epub 2006 Dec 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17179949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bucci M, Gratton JP, Rudic RD, Acevedo L, Roviezzo F, Cirino G, et al. In vivo delivery of the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain inhibits nitric oxide synthesis and reduces inflammation. Nat Med. 2000;6:1362–1367. - PubMed
-
- Bucci M, Roviezzo F, Brancaleone V, Lin MI, Di Lorenzo A, Cicala C, et al. Diabetic mouse angiopathy is linked to progressive sympathetic receptor deletion coupled to an enhanced caveolin-1 expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:721–726. - PubMed
-
- Carman CV, Lisanti MP, Benovic JL. Regulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinases by caveolin. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:8858–8864. - PubMed
-
- Chernogubova E, Hutchinson DS, Nedergaard J, Bengtsson T. Alpha1- and beta1-adrenoceptor signaling fully compensated for adrenoceptor deficiency in brown adipocyte norepinephrine-stimulated glucose uptake. Endocrinology. 2005;146:2271–2284. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

