A phase I trial of the selective oral cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor seliciclib (CYC202; R-Roscovitine), administered twice daily for 7 days every 21 days
- PMID: 17179992
- PMCID: PMC2360206
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603509
A phase I trial of the selective oral cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor seliciclib (CYC202; R-Roscovitine), administered twice daily for 7 days every 21 days
Abstract
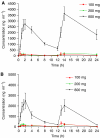
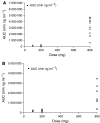
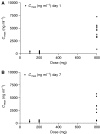
Seliciclib (CYC202; R-roscovitine) is the first selective, orally bioavailable inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases 1, 2, 7 and 9 to enter clinical trial. Preclinical studies showed antitumour activity in a broad range of human tumour xenografts. A phase I trial was performed with a 7-day b.i.d. p.o. schedule. Twenty-one patients (median age 62 years, range: 39-73 years) were treated with doses of 100, 200 and 800 b.i.d. Dose-limiting toxicities were seen at 800 mg b.i.d.; grade 3 fatigue, grade 3 skin rash, grade 3 hyponatraemia and grade 4 hypokalaemia. Other toxicities included reversible raised creatinine (grade 2), reversible grade 3 abnormal liver function and grade 2 emesis. An 800 mg portion was investigated further in 12 patients, three of whom had MAG3 renograms. One patient with a rapid increase in creatinine on day 3 had a reversible fall in renal perfusion, with full recovery by day 14, and no changes suggestive of renal tubular damage. Further dose escalation was precluded by hypokalaemia. Seliciclib reached peak plasma concentrations between 1 and 4 h and elimination half-life was 2-5 h. Inhibition of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation was not demonstrated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. No objective tumour responses were noted, but disease stabilisation was recorded in eight patients; this lasted for a total of six courses (18 weeks) in a patient with ovarian cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Alvi AJ, Austen B, Weston VJ, Fegan C, MacCallum D, Gianella-Borradori A, Lane DP, Hubank M, Powell JE, Wei W, Taylor AMR, Moss PAH, Tatjana Stankovic T (2005) A novel Cdk inhibitor, CYC202 (R-roscovitine), overcomes the defect in p53-dependent apoptosis in B-CLL by down-regulation of genes involved in transcription regulation and survival. Blood 105: 4484–4491 - PubMed
-
- Bach S, Knockaert M, Reinhardt J, Lozach O, Schmitt S, Baratte B, Koken M, Coburn SP, Tang L, Jiang T, Liang DC, Galons H, Dierick JF, Pinna LA, Meggio F, Tozke F, Schachtele C, Lerman AS, Carno A, Wan Y, Gray N, Meijer L (2005) Roscovitine targets: protein kinase and pyridoxal kinase. J Biol Chem 280: 31208–31219 - PubMed
-
- De Azevedo WF, Leclerc S, Meijer L, Havlicek L, Strnad M, Kim SH (1997) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues: crystal structure of human cdk2 complexed with roscovitine. Eur J Biochem 243: 518–526 - PubMed
-
- De la Motte S, Gianella-Borradori A (2004) Pharmacokinetic model of R-roscovitine and its metabolite in healthy male subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 42: 232–239 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

