Antisense oligonucleotides containing locked nucleic acid improve potency but cause significant hepatotoxicity in animals
- PMID: 17182632
- PMCID: PMC1802611
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl1071
Antisense oligonucleotides containing locked nucleic acid improve potency but cause significant hepatotoxicity in animals
Abstract
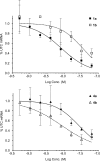
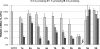
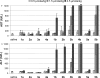
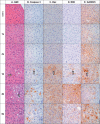
A series of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) containing either 2'-O-methoxyethylribose (MOE) or locked nucleic acid (LNA) modifications were designed to investigate whether LNA antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) have the potential to improve upon MOE based ASO therapeutics. Some, but not all, LNA containing oligonucleotides increased potency for reducing target mRNA in mouse liver up to 5-fold relative to the corresponding MOE containing ASOs. However, they also showed profound hepatotoxicity as measured by serum transaminases, organ weights and body weights. This toxicity was evident for multiple sequences targeting three different biological targets, as well as in mismatch control sequences having no known mRNA targets. Histopathological evaluation of tissues from LNA treated animals confirmed the hepatocellular involvement. Toxicity was observed as early as 4 days after a single administration. In contrast, the corresponding MOE ASOs showed no evidence for toxicity while maintaining the ability to reduce target mRNA. These studies suggest that while LNA ASOs have the potential to improve potency, they impose a significant risk of hepatotoxicity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hepatotoxicity of high affinity gapmer antisense oligonucleotides is mediated by RNase H1 dependent promiscuous reduction of very long pre-mRNA transcripts.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Mar 18;44(5):2093-109. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1210. Epub 2015 Nov 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26553810 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of hepatic transcription profiles of locked ribonucleic acid antisense oligonucleotides: evidence of distinct pathways contributing to non-target mediated toxicity in mice.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Mar;138(1):234-48. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft278. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24336348
-
Short antisense oligonucleotides with novel 2'-4' conformationaly restricted nucleoside analogues show improved potency without increased toxicity in animals.J Med Chem. 2009 Jan 8;52(1):10-3. doi: 10.1021/jm801294h. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19086780
-
An overview of sugar-modified oligonucleotides for antisense therapeutics.Chem Biodivers. 2011 Sep;8(9):1616-41. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201100081. Chem Biodivers. 2011. PMID: 21922654 Review.
-
Locked nucleic acid oligonucleotides: the next generation of antisense agents?BioDrugs. 2007;21(4):235-43. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200721040-00004. BioDrugs. 2007. PMID: 17628121 Review.
Cited by
-
From evolution to revolution: miRNAs as pharmacological targets for modulating cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Sep;75:60-72. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.02.005. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23435093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, Biophysical and Biological Evaluation of Splice-Switching Oligonucleotides with Multiple LNA-Phosphothiotriester Backbones.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Oct 30;146(43):29773-29781. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c11402. Epub 2024 Oct 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 39401255 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial genetic polymers against human pathologies.Biol Direct. 2022 Dec 6;17(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13062-022-00353-7. Biol Direct. 2022. PMID: 36474260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticle delivery of a microRNA-145 inhibitor improves experimental pulmonary hypertension.J Control Release. 2015 Jul 28;210:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.05.261. Epub 2015 May 13. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25979327 Free PMC article.
-
Splice-Modulating Antisense Oligonucleotides as Therapeutics for Inherited Metabolic Diseases.BioDrugs. 2024 Mar;38(2):177-203. doi: 10.1007/s40259-024-00644-7. Epub 2024 Jan 22. BioDrugs. 2024. PMID: 38252341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vitravene Study Group. Randomized dose-comparison studies of intravenous fomiversen for treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis that has reactivated or is persistently active despite other therapies in patients with AIDS. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002;133:475–483. - PubMed
-
- Eckstein F. Phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides: what is their origin and what is unique about them? Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 2000;10:117–121. - PubMed
-
- Geary R.S., Yu R.Z., Levin A.A. Pharmacokinetics of phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2001;2:562–573. - PubMed
-
- Lima W.F., Nichols J.G., Wu H., Prakash T.P., Migawa M.T., Wyrzykiewicz T.K., Bhat B., Crooke S.T. Structural requirements at the catalytic site of the heteroduplex substrate for human RNase H1 catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:36317–36326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

